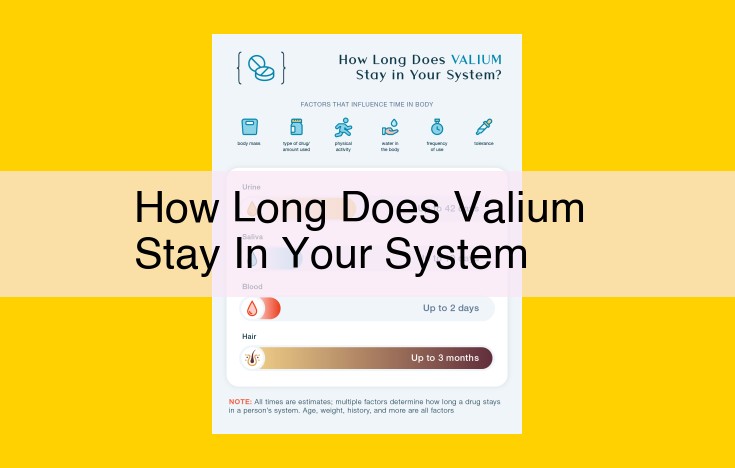
Valium’s detectability in one’s system depends on physiological factors like metabolism, age, and weight, as well as drug-related factors like dosage and frequency of use. It can be detected in urine for up to 5 days, in blood for 48-120 hours, and in saliva for 24-48 hours. External factors such as hydration levels, exercise, and concurrent medication use can also impact detection times. Understanding these factors is essential for responsible Valium use and accurate detection practices.
Factors Influencing Valium Detection: Unraveling the Enigma
Valium, a potent benzodiazepine, often prescribed for anxiety and sleep disorders, leaves a subtle trail in our bodies. Understanding the intricate tapestry of factors that weave this detectability is crucial.
Physiological Factors:
- Metabolism: Each person’s unique enzymatic machinery governs the rate of Valium breakdown. Some individuals metabolize it swiftly, while others hold on to it a bit longer.
- Weight and Body Fat: Individuals with a higher body mass tend to have larger distribution volumes, leading to lower detectable Valium levels in their blood and urine.
- Kidney Function: The kidneys play a pivotal role in Valium excretion. Impaired kidney function can slow the elimination process, prolonging its detectability.
Drug-Related Factors:
- Dosage: The amount of Valium consumed is a primary determinant of detectable levels. Higher doses require a longer timeframe for the body to clear.
- Frequency of Use: Chronic Valium use can alter its pharmacokinetics, making it more persistent in the body. The drug’s elimination pathways may become saturated, leading to accumulation.
- Concurrent Medication Use: Certain medications, such as cimetidine and erythromycin, can inhibit Valium metabolism, extending its detectability.
Unveiling these factors empowers individuals seeking a more comprehensive understanding of Valium’s presence within their bodies. It’s paramount to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance when navigating the complexities of medication use.
Detection Times of Valium in Bodily Fluids
Urine:
- Valium can be detected in urine for up to 5 days after last use.
- This is the most common method of detecting Valium because it is non-invasive and can be collected easily.
Blood:
- Valium can be detected in blood for up to 2 days after last use.
- Blood tests are more sensitive than urine tests, but they are also more invasive and expensive.
Saliva:
- Valium can be detected in saliva for up to 24 hours after last use.
- Saliva testing is becoming more common because it is non-invasive and can provide rapid results.
Factors Affecting Detection Times:
The detection time of Valium can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Dosage: Higher doses of Valium will result in longer detection times.
- Frequency of use: Regular use of Valium will lead to higher levels in the body and longer detection times.
- Metabolism: People with faster metabolisms will clear Valium from their system more quickly, resulting in shorter detection times.
- Age: Older adults may have longer detection times due to decreased kidney function.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated can help to flush Valium out of the system and reduce detection times.
Understanding the detection times of Valium is crucial for individuals who are undergoing drug testing or who are concerned about the potential consequences of Valium use.
Factors Affecting Valium Detection Times
When it comes to detecting Valium in the body, external factors can play a significant role in influencing how long it remains detectable. These factors can impact the rate at which Valium is metabolized and excreted, affecting the duration of its presence in various bodily fluids.
Hydration Levels
Staying hydrated is crucial for reducing the detection time of Valium. Water helps flush out the drug from the body through urine, effectively shortening its presence. Consuming plenty of fluids, especially water, can accelerate Valium elimination and reduce its detectability.
Exercise
Physical activity can also affect Valium detection times. Exercise increases blood flow and metabolism, which can hasten the drug’s breakdown and removal from the body. Engaging in moderate to intense exercise post-Valium intake can potentially shorten its detectability window.
Concurrent Medication Use
Certain medications can interact with Valium, altering its detection times. For instance, combining Valium with other depressants like alcohol or opioids can prolong its detectability by impairing its metabolism. Conversely, medications that speed up metabolism, such as certain antibiotics, may shorten Valium’s detection time.
Understanding these external factors and their impact on Valium detectability is essential for individuals concerned about drug testing or seeking to minimize its presence in their system.
Entities Involved in Valium Detection
Understanding the entities involved in Valium detection is crucial for interpreting test results and making informed decisions.
Physicians:
Physicians are the primary healthcare professionals responsible for prescribing and monitoring Valium use. They assess patients’ medical history, prescribe appropriate dosages, and order tests to monitor Valium levels. Their expertise is vital in ensuring safe and effective Valium administration.
Pharmacists:
Pharmacists play a key role in dispensing Valium and providing patient education. They verify prescriptions, counsel patients on proper usage, and monitor potential drug interactions. Their knowledge of Valium’s effects and safety guidelines helps ensure responsible use.
Toxicologists:
Toxicologists specialize in the analysis and interpretation of toxic substances in the body. They conduct laboratory tests to measure Valium levels in various bodily fluids, such as urine and blood. Their expertise aids in diagnosing Valium intoxication, assessing drug interactions, and providing evidence for legal proceedings.
Addiction Specialists:
Addiction specialists, including addiction doctors and counselors, work with individuals struggling with Valium addiction. They assess the severity of addiction, develop treatment plans, and monitor recovery progress. Their understanding of Valium’s addiction potential and withdrawal symptoms is crucial for successful treatment.
By collaborating with these medical entities, patients can receive accurate Valium detection, personalized treatment plans, and support in overcoming addiction. It’s essential to consult with these professionals to ensure optimal health outcomes and informed decision-making regarding Valium use.
Implications of Detectable Valium Levels: Employment, Legal, and Treatment Concerns
Valium, a widely prescribed anti-anxiety medication, remains detectable in the body for a variable duration. Understanding the implications of detectable Valium levels is crucial for individuals using the medication, employers, legal authorities, and addiction specialists.
Employment: Many employers conduct urine or blood testing to screen for drug use in potential or current employees. Detectable Valium levels can result in disqualification from job positions, particularly those involving safety-sensitive responsibilities. Individuals should disclose Valium use to potential employers to avoid misunderstandings and unfavorable outcomes.
Legal Matters: In legal proceedings, such as child custody disputes or DUI cases, Valium detection can influence decisions. Detectable Valium levels may cast doubt on an individual’s fitness or sobriety, potentially affecting legal outcomes. Individuals should be aware of the potential consequences before engaging in activities where Valium detection may be relevant.
Addiction Treatment: For individuals seeking addiction treatment, detectable Valium levels can impact their treatment plan. Valium is a controlled substance, and detectable levels indicate ongoing use. This information can guide treatment providers in tailoring interventions to address both Valium use and other underlying substance abuse issues.
It is important to note that the consequences of detectable Valium levels vary depending on the specific context and individual circumstances. Transparent communication with healthcare professionals, honesty in employment applications, and awareness of legal implications can help mitigate potential challenges associated with Valium detection.
Tips for Reducing Valium Detectability
If you’re concerned about the detectability of Valium in your system, there are several practical tips you can follow to reduce its presence and make it harder to detect.
1. Monitor Your Dosage Carefully
The amount of Valium you take directly influences its detectability. Stick to the prescribed dosage and avoid taking excessive amounts. Higher doses will lead to higher levels of Valium in your body and longer detection times.
2. Stay Adequately Hydrated
Drinking plenty of fluids, particularly water, helps to flush Valium out of your system. When hydrated, your body produces more urine, which dilutes the concentration of Valium present. Aim to drink eight to ten glasses of water per day.
3. Avoid Concurrent Substance Use
Certain substances can interfere with Valium metabolism and prolong its detectability. Avoid consuming alcohol, caffeine, and grapefruit products, as these can slow down Valium breakdown.
4. Exercise Regularly
Moderate exercise can help increase your metabolism and speed up the elimination of Valium from your body. Aim for 30 minutes of light to moderate exercise most days of the week.
5. Eat a Balanced Diet
A healthy diet can support your body’s detoxification processes. Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of fat.
By following these tips, you can reduce the detectability of Valium in your system. However, it’s crucial to remember that Valium detection times vary from person to person, and these tips do not guarantee that Valium will be undetectable. If you have any concerns or questions about Valium detection, it’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional.