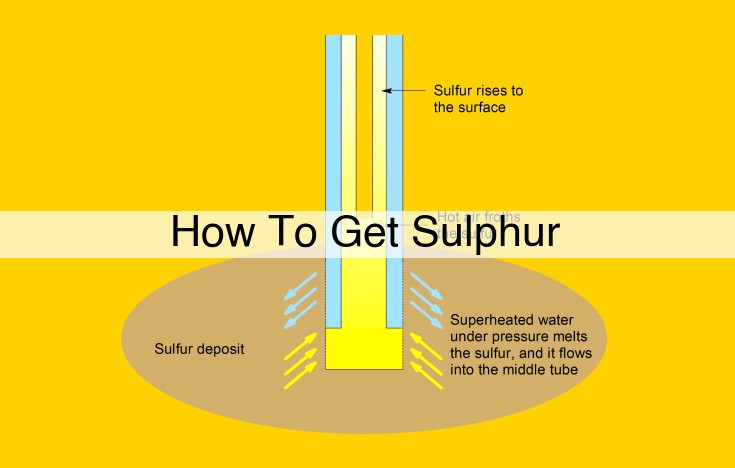
Sulphur, an essential element, is obtained from volcanic deposits and oil and gas production. Elemental sulphur is used in fertiliser, chemicals, and rubber, while sulphur compounds find applications in industrial processes. Sulphur mining and processing can impact the environment, releasing pollutants like sulphur dioxide and sulphuric acid. Balancing industrial use with sustainable practices is crucial to minimise environmental impact while harnessing sulphur’s benefits.
Sulphur: A Vital Element in Our World
In the tapestry of our planet’s chemistry, sulphur stands as an unsung hero, essential for a vast array of industries and processes that sustain our daily lives. From the fertilizers that nourish our crops to the rubber in our tires, sulphur plays an indispensable role in shaping our modern world.
Sulphur’s Diverse Applications
Sulphur finds its applications in a multitude of industries. Its raw form, known as elemental sulphur, is primarily used in the production of fertilizers. It combines with other elements to create sulphate fertilizers, which are crucial for crop growth and food production.
Beyond agriculture, sulphur is also a key ingredient in various industrial chemicals, such as sulphuric acid. This acid is used in the manufacture of batteries, dyes, and textiles, among countless other products. Moreover, sulphur is a vital component in the production of rubber, a material essential for tires, footwear, and other applications.
Elemental Sulphur: A Versatile Raw Material
Elemental sulphur, a naturally occurring substance, plays a crucial role in countless industries and applications. This versatile raw material is found in volcanic deposits and can also be extracted from oil and gas production as a byproduct.
The wide range of applications for elemental sulphur stems from its unique properties. It is a key ingredient in the production of fertilizers, providing essential nutrients to crops that feed the world’s population. In addition, elemental sulphur serves as a vital component in the manufacturing of industrial chemicals, such as sulphuric acid, which is used in various sectors including mining, refining, and water treatment. The rubber industry also relies heavily on elemental sulphur, which acts as a vulcanizing agent, strengthening and improving the durability of rubber products like tires.
However, the mining and processing of elemental sulphur can have potential environmental implications. Sulphur mining operations may disrupt ecosystems and release harmful pollutants into the environment. Similarly, improper handling and processing of elemental sulphur can lead to the emission of sulphur dioxide, a gas that contributes to air pollution.
To minimize these impacts, it is paramount to implement sustainable practices throughout the elemental sulphur life cycle. Responsible mining operations, coupled with efficient processing techniques, can significantly reduce environmental concerns. Moreover, recycling and reusing elemental sulphur can curb the demand for new mining and help conserve natural resources.
It is evident that elemental sulphur is an invaluable raw material with a wide array of applications. By understanding its sources, applications, and potential environmental impacts, we can harness this resource responsibly while ensuring a sustainable future.
Sulphur Compounds: Diverse and Complex
Sulphur, a versatile element, forms a multitude of compounds with varying properties and plays a crucial role in various industries. Among these compounds are hydrogen sulphide, sulphur dioxide, and sulphuric acid, each holding unique significance and environmental implications.
Hydrogen Sulphide: The Pungent Odour
Hydrogen sulphide is a colourless gas with a distinctive unpleasant odour reminiscent of rotten eggs. It is primarily emitted from natural sources such as volcanic eruptions and biological decomposition processes in wetlands.
*Industrial activities, including petroleum refining and wastewater treatment, also contribute to its release into the atmosphere. Exposure to hydrogen sulphide can irritate the eyes, throat, and respiratory tract.
Sulphur Dioxide: A Major Air Pollutant
Sulphur dioxide is a pungent gas with a choking odour. It is predominantly released during the combustion of fossil fuels and industrial processes involving sulphur-containing materials.
This gas is a significant contributor to *air pollution and acid rain. It can cause respiratory problems, particularly in vulnerable populations such as asthmatics.
Sulphuric Acid: The Versatile Industrial Chemical
Sulphuric acid is a highly corrosive liquid with a wide range of applications in industries such as fertilizer production, metal processing, and battery manufacturing.
It is primarily produced from *sulphur dioxide and is also found in acid rain. Sulphuric acid can have adverse effects on human health and the environment, leading to skin burns and vegetation damage.
The release of sulphur compounds into the atmosphere poses significant environmental concerns. These compounds contribute to acid rain, air pollution, and climate change. Acid rain damages forests, lakes, and buildings, while air pollution can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems.
Managing sulphur emissions is crucial to protect human health and the environment. Strategies such as flue gas desulphurization, using low-sulphur fuels, and improving industrial processes can help minimize the release of these compounds.
Sources of Sulphur: Interplay Between Elemental and Compounds
Sulphur, an element of vital importance in various industries and natural processes, can exist in both elemental form and as diverse compounds. While elemental sulphur serves as a versatile raw material, sulphur compounds play a significant role in the global sulphur cycle and environmental dynamics.
Elemental Sulphur: The Building Block
Elemental sulphur, the purest form of this element, can be sourced from volcanic deposits or as a byproduct of oil and gas production. Its wide-ranging applications include:
- Fertilizer production: Sulphur is a crucial component in fertilizers, enhancing soil fertility for agricultural productivity.
- Industrial chemicals: Elemental sulphur is used to manufacture a variety of chemicals, such as sulphuric acid, a key ingredient in paints, dyes, and batteries.
- Rubber manufacturing: Sulphur undergoes vulcanization, a process that strengthens and improves the elasticity of rubber.
Sulphur Compounds: A Spectrum of Forms
Sulphur compounds, formed by the combination of sulphur with other elements, occur naturally and through industrial processes. Common types include:
- Hydrogen sulphide: A toxic gas released from volcanic eruptions and decomposition processes, it can pose risks to human health and the environment.
- Sulphur dioxide: A major air pollutant, sulphur dioxide primarily results from fossil fuel combustion and industrial activities.
- Sulphuric acid: A corrosive acid found in acid rain, it is produced by the reaction of sulphur dioxide with atmospheric water and oxygen.
The Sulphur Cycle: A Continuous Transformation
Elemental sulphur and sulphur compounds are interconnected within the sulphur cycle. Elemental sulphur can be used to produce sulphur compounds, such as sulphuric acid, through industrial processes. Natural processes, like volcanic eruptions and biological decomposition, also generate sulphur compounds.
The relative contributions of elemental sulphur and sulphur compounds to the overall sulphur cycle vary depending on natural and anthropogenic factors. However, both forms play critical roles in maintaining the balance of this important element in the Earth’s ecosystems.