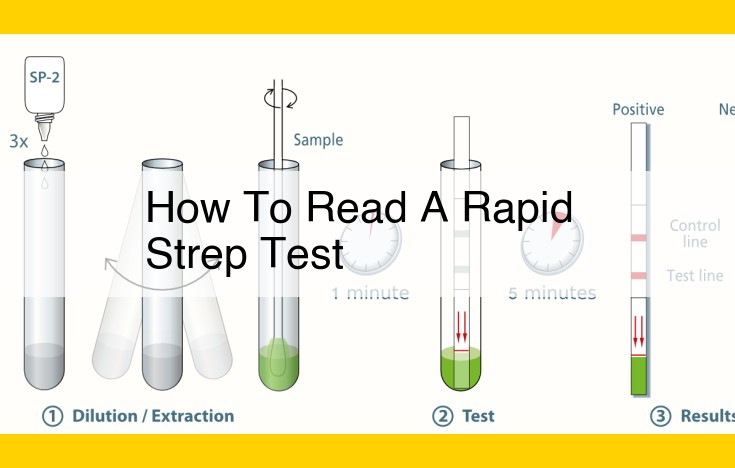
To interpret a rapid strep test, check for the presence or absence of colored bands on the test strip. A single positive (+) band, indicating the presence of group A streptococci (GAS), suggests a positive result for strep throat. Conversely, a single negative (-) band rules out GAS infection. If there is no band or multiple bands, the test is invalid and must be repeated. The presence of a control band (C) indicates that the test is working correctly. Physicians and nurses play key roles in administering and interpreting the test.
Entities Involved in the Rapid Strep Test: A Physician’s Perspective
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in Diagnosing Strep Throat
Imagine yourself with a sore throat that just won’t go away. You’re miserable and wondering if it’s just a common cold or something more serious. Your doctor suspects strep throat, a bacterial infection that can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, swollen lymph nodes, and difficulty swallowing. To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor performs a rapid strep test, a simple and quick procedure that can tell them if you have strep throat in a matter of minutes.
Administering the Rapid Strep Test
Healthcare professionals, such as physicians and nurses, are trained to administer the rapid strep test. They use a special swab to gently collect a sample from the back of your throat or tonsils. This sample is then placed on a test strip, which contains chemicals that react with specific markers of the strep bacteria.
Interpreting the Test Results
Positive results are indicated by the appearance of two colored bands on the test strip: a control band (which ensures that the test is working properly) and a test band (which indicates the presence of strep). A negative result is indicated by the appearance of only the control band.
Guiding Treatment Decisions
Based on the test results, your doctor will decide on the best treatment for your sore throat. If the test is positive, you will likely be prescribed antibiotics to clear up the bacterial infection. If the test is negative, your doctor may recommend other tests or treatments to determine the cause of your symptoms.
The Importance of Accuracy
Accurate test results are crucial for ensuring proper diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare professionals are responsible for ensuring that the test is administered and interpreted correctly, providing patients with the peace of mind that their symptoms are being addressed appropriately.
The Rapid Strep Test: A Comprehensive Overview
1. Entities Involved in Rapid Strep Test
The rapid strep test is a quick and convenient way to diagnose Streptococcus pyogenes (strep throat) infections. Let’s explore the key entities involved in this test:
Physicians:
Physicians play a vital role in administering the test and interpreting the results. They determine the patient’s symptoms, order the test, and explain the findings.
Rapid Strep Test Kit:
The test kit contains the necessary components for the procedure, including:
- Specimen swabs: Used to collect a sample from the back of the throat.
- Extraction reagent: Prepares the sample for testing.
- Test strip: Contains antibodies that react with strep bacteria.
- Control band (C): Ensures the test is working properly.
2. Entities Directly Related to Rapid Strep Test
Nurses:
Nurses assist physicians by:
- Collecting the throat swab sample.
- Administering the test.
Negative (-) Band:
A negative result indicates the absence of S. pyogenes bacteria in the sample.
Positive (+) Band:
A positive result indicates the presence of S. pyogenes bacteria, suggesting a strep throat infection.
3. Entities Indirectly Related to Rapid Strep Test
Physician Assistants:
In some settings, physician assistants may be authorized to administer the rapid strep test.
Laboratory:
Laboratories can be involved in verifying the test results if necessary.
Manufacturer of Rapid Strep Test Kit:
Companies or organizations produce and distribute the test kits.
Understanding the Positive (+) Band in Rapid Strep Tests
In the realm of healthcare, the rapid strep test stands as a valuable tool for diagnosing streptococcal pharyngitis, commonly known as strep throat. This quick and convenient test provides crucial information within minutes, guiding medical professionals toward appropriate treatment.
At the heart of the rapid strep test lies a test strip impregnated with antibodies specific to Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria responsible for strep throat. When a specimen swab from the patient’s throat is applied to the test strip, it interacts with the antibodies. If Streptococcus pyogenes is present, a positive result emerges in the form of a colored band (positive band) next to the letter “T” on the test strip.
A positive result serves as a clear indication that the patient has strep throat. This finding has significant implications for the course of treatment. Strep throat typically requires a course of antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria and prevent potential complications. By accurately identifying strep throat, healthcare providers can initiate prompt antibiotic therapy, reducing the duration of symptoms and the risk of bacterial spread.
Additional points you may want to mention:
- The presence of a positive band should be considered reliable evidence of strep throat, with an accuracy rate of over 90%.
- False-negative results can occur, so further testing may be necessary if clinical suspicion is high despite a negative result.
- It’s crucial for patients to complete the prescribed course of antibiotics even if symptoms improve quickly to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria.
- If left untreated, strep throat can lead to serious complications, such as rheumatic fever or kidney infections.
The Role of Nurses in the Rapid Strep Test
The rapid strep test is a valuable tool for diagnosing streptococcal pharyngitis, commonly known as strep throat. Nurses play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of this test by assisting with specimen collection and test administration.
Specimen Collection
Nurses are responsible for collecting a swab sample from the back of the patient’s throat. This involves using a sterile swab to gently rub the tonsils and pharynx. The sample is then transferred to a test kit for analysis. It is essential that the nurse collects an adequate sample that contains sufficient bacteria for an accurate result.
Test Administration
After the specimen has been collected, the nurse inserts the swab into the test kit. The kit contains a reagent that helps release the bacteria from the sample. The sample then flows onto a test strip, which contains antibodies that react with the bacteria. If the bacteria are present, a colored band will appear on the test strip, indicating a positive result.
Interpretation
The nurse then interprets the test results based on the presence or absence of the colored band. A positive result indicates that the patient has strep throat and should be treated with antibiotics. A negative result suggests that the patient does not have strep throat and other causes should be considered.
Additional Nursing Responsibilities
In addition to specimen collection and test administration, nurses may also:
- Explain the test procedure to patients
- Answer patients’ questions about the test and its results
- Provide emotional support to patients during the testing process
- Document the test results and communicate them to the physician
Nurses play a vital role in the accurate and efficient performance of the rapid strep test. Their expertise in specimen collection, test administration, and interpretation ensures that patients receive the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment for streptococcal pharyngitis.
Entities Involved in Rapid Strep Test
Entities Directly Related to Rapid Strep Test
Specimen Swab
The specimen swab, an essential component of the rapid strep test, plays a pivotal role in obtaining an accurate sample for testing. Proper collection technique is crucial to ensure a representative sample of the target bacteria (Streptococcus pyogenes).
Collection Process
- Choose the correct swab: Sterile cotton or rayon-tipped swabs are typically used for collecting samples from the throat or tonsils.
- Swab the target area: Insert the swab into the back of the throat or against the tonsils and gently swab the affected area. Rotate the swab several times to collect a sufficient sample.
- Avoid contact with other surfaces: Ensure the swab does not touch the tongue, teeth, or gums, as this can contaminate the sample.
Importance of Proper Collection
A suitable specimen is paramount for accurate test results. Insufficient or contaminated samples can lead to false negatives or inconclusive results. Proper swabbing technique minimizes the risk of contamination and ensures the presence of a sufficient amount of bacteria for detection.
Consequences of Inadequate Sample Collection
Inadequate sample collection can result in:
- Incorrect diagnosis
- Inappropriate treatment decisions
- Delayed recovery from strep throat
- Potential spread of the infection
By following the proper collection procedure and using a sterile swab, healthcare providers can obtain an optimal sample for accurate and reliable rapid strep test results.
The Negative Band: Unveiling the Absence of Streptococcus
In the realm of rapid strep testing, the negative (-) band plays a pivotal role in unraveling the enigmatic absence of Streptococcus, the culprit behind infections like tonsillitis. Negative results provide a sense of relief, indicating that the throat swab collected from the patient is devoid of the troublesome bacteria.
Just as a bright sun pierces through the clouds, a negative outcome shines a ray of hope. It suggests that the sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes may stem from a different source, such as a virus or other infection. In this scenario, antibiotics, typically prescribed for strep infections, would not be effective and could lead to unnecessary side effects.
Moreover, a negative band helps physicians avoid overprescribing antibiotics, which can contribute to antibiotic resistance, a growing global health concern. Resisting antibiotic resistance is paramount to preserving their efficacy for when they are truly needed.
Thus, the negative band serves as a beacon of clarity, guiding physicians in their diagnostic journey. It empowers them to make informed decisions, tailoring treatments to the specific needs of their patients.
The Rapid Strep Test: A Comprehensive Guide to Entities Involved
Entities Directly Related to the Rapid Strep Test
Among the key entities directly involved in the rapid strep test are healthcare professionals, nurses, and the test kit itself. Physicians play a crucial role in administering the test and interpreting the results. They determine the necessity of the test based on symptoms and examine the results to guide appropriate treatment.
Nurses, in collaboration with physicians, assist in the crucial process of specimen collection. Using a specimen swab, they gently collect a sample from the tonsillar swab/throat swab site. This sample is then applied to the test strip, which houses antibodies that react with specific antigens in the sample.
The test strip displays two distinct bands: the positive (+) band and the negative (-) band. A positive result, indicated by the presence of the positive band, suggests the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria causing tonsillitis – an infection of the tonsils. A negative result, on the other hand, indicates the absence of the bacteria and rules out strep throat as the cause of symptoms.
Understanding the Rapid Strep Test: Entities Involved
1. Entities Directly Involved in the Rapid Strep Test (Score 10)
- Physicians: Healthcare professionals who administer and interpret the test results, playing a crucial role in diagnosing and treating streptococcal infections.
- Rapid strep test kit: The device used to perform the test, consisting of a test strip, extraction reagent, and other components that facilitate the identification of Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Positive (+) band: Indicates the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes in the sample, suggesting a positive diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat).
2. Entities Indirectly Related to the Rapid Strep Test (Score 8)
- Nurses: Assist healthcare professionals in collecting specimen swabs and administering the test, ensuring proper sample handling.
- Specimen swab: A cotton-tipped or other type of swab used to collect a sample from the tonsillar/throat area for testing.
- Negative (-) band: Indicates the absence of Streptococcus pyogenes in the sample, suggesting a result that may not require antibiotic treatment.
- Physician assistants: In some cases, authorized physician assistants may administer the rapid strep test and interpret the results.
- Extraction reagent: A solution used to prepare the sample by breaking down cell walls and releasing antigens for easier detection.
- Test strip: A plastic or paper strip containing antibodies that react with Streptococcus pyogenes antigens, displaying the test results as colored bands.
- Control band (C): A reference band on the test strip that ensures the test is functioning correctly.
- Laboratory: May be involved in verifying the test results if necessary, particularly in cases where the results are inconclusive or contradictory.
- Manufacturer of rapid strep test kit: Companies or organizations responsible for producing and distributing the test kits used for rapid strep testing.
Understanding Tonsillitis: The Focus of the Rapid Strep Test
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, two small glands located at the back of the throat. The condition is commonly caused by bacterial or viral infections, with Streptococcus pyogenes being the most common bacterial culprit. The rapid strep test is a quick and effective tool for diagnosing streptococcal tonsillitis, allowing physicians to prescribe appropriate treatment and prevent potential complications.
Physician assistants: Highlight their potential involvement in the test if they are authorized to do so.
Entities Involved in Rapid Strep Test
1. Healthcare Professionals
- Physicians: Diagnose and prescribe treatment based on test results.
- Nurses: Assist with specimen collection and test administration.
2. Test Kit Components
- Rapid strep test kit: Contains components for sample collection, extraction, and display of results.
- Specimen swab: Collects a sample from the throat or tonsils.
- Extraction reagent: Prepares the sample for testing.
- Test strip: Displays the test results as positive (+) or negative (-) bands.
3. Purpose and Interpretation
- Positive (+) band: Indicates the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria, which causes strep throat.
- Negative (-) band: Indicates the absence of S. pyogenes bacteria.
- Control band (C): Ensures the test is working properly.
4. Additional Entities
- Physician assistants (PAs): May administer the test if authorized to do so.
- Laboratory: May verify test results if necessary.
- Manufacturer: Produces the rapid strep test kit.
Physician Assistants: A Potential Role
Physician assistants (PAs) are medical professionals who can provide a wide range of healthcare services, including administering diagnostic tests. Their training includes instruction in rapid strep testing, and they may be authorized to perform the test in many jurisdictions. This allows PAs to play a valuable role in the diagnosis of strep throat, especially in areas where physician availability is limited.
The rapid strep test is a valuable tool for diagnosing strep throat. It involves several entities, including healthcare professionals, test kit components, and related entities such as laboratories and manufacturers. By understanding the roles and responsibilities of each entity involved, we can ensure the accurate and effective use of this important diagnostic test.
The Role of Extraction Reagent in Rapid Strep Testing
In the realm of diagnosing strep throat, the rapid strep test stands as a reliable and swift method. This diagnostic tool relies on a harmonious interplay of various entities, including the extraction reagent, which plays a pivotal role in preparing the sample for testing.
The Extraction Reagent: A Gateway to Accurate Results
The extraction reagent is a crucial component in the rapid strep test process. Its primary function is to extract the antigens from the patient’s throat swab. These antigens are proteins specific to Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacterium responsible for strep throat.
The Extraction Process: A Delicate Dance
The extraction process commences with the swabbing of the patient’s throat. The swab, saturated with the collected sample, is then immersed in the extraction reagent. This reagent contains a buffering solution that helps maintain the proper pH level for optimal antigen detection.
As the swab is gently swirled, the extraction reagent *disrupts** the bacterial cell membranes, releasing the antigens into the solution. The reagent also *neutralizes** any inhibitors present in the sample, ensuring that they do not interfere with the test results.
Preparing for the Test: A Journey from Extract to Test Strip
Once the antigens have been extracted, the solution is ready for the test strip. This diagnostic strip contains antibodies specific to Streptococcus pyogenes antigens. The extracted sample is dispensed onto the test strip, where it migrates through the membrane.
As the sample travels across the membrane, the antigens bind to their corresponding antibodies. This interaction triggers a reaction that generates a visible color change on the test strip. The presence or absence of this color change determines whether the patient is positive or negative for strep throat.
The extraction reagent serves as a vital cog in the rapid strep test, ensuring the accuracy of the results. By effectively extracting the antigens from the throat swab, this reagent paves the way for the detection of Streptococcus pyogenes antigens and the subsequent diagnosis of strep throat.
Test strip: Describe the process of the test strip and how it displays the results.
Entities Involved in Rapid Strep Test
Test Strip: Unraveling the Mystery
At the heart of the rapid strep test lies a humble yet powerful component: the test strip. This small but mighty strip holds the key to unveiling the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes, the pesky bacteria that causes strep throat.
The test strip is engineered with a clever design that combines antibodies with chromogenic substances. Antibodies are proteins that are tailor-made to recognize specific antigens, which are unique molecules found on the surface of bacteria. In this case, the antibodies on the strip are designed to latch onto the Streptococcal antigens.
When a sample containing Streptococcus pyogenes is applied to the test strip, these antibodies spring into action, forming an unbreakable bond with the antigens. This binding reaction triggers a chain of events that leads to the appearance of a visible band on the strip.
Inside the strip, an invisible chromogen waits patiently. As the antibodies capture the antigens, they draw the chromogen along with them. This chromogen is a color-producing substance that, upon further chemical reactions, transforms into a vibrant red line.
This line, known as the test band, serves as a resounding “yes” to the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes. Its visibility indicates that the patient’s sore throat is most likely caused by strep bacteria, providing valuable information for both the patient and the healthcare provider.
However, there’s another crucial band on the test strip: the control band. This band appears even when there are no strep bacteria present, confirming that the test is working properly. It acts as a safety check, assuring healthcare professionals that the test is reliable and the results can be trusted.
So, as you gaze upon the humble test strip, remember that its simplicity conceals a captivating tale of scientific ingenuity and diagnostic precision. It serves as a silent witness, guiding decisions and offering invaluable insights into the world of strep throat detection.
Control Band (C): The Unsung Hero of Rapid Strep Tests
In the realm of healthcare diagnostics, the rapid strep test stands out as a reliable and efficient tool for detecting Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria, the culprit behind the dreaded strep throat. However, behind the scenes, there’s an unsung hero that plays a crucial role in ensuring the test’s accuracy: the control band.
What is the Control Band?
The control band, often labeled as “C,” serves as a beacon of reliability in the test cassette. It consists of a pink or blue line that appears when the test functions as intended. Its presence signifies that the sample has been properly applied and processed, and the test strip is reacting appropriately.
Why is the Control Band Important?
The control band is not just a formality; it’s an essential diagnostic tool. Its absence or presence provides valuable information about the test performance:
-
Valid Test: If the control band is present, it confirms that the test components, including antibodies, reagents, and test strip, are functioning correctly. This serves as a reassurance that the test result is reliable.
-
Invalid Test: In contrast, if the control band is absent, it indicates a problem with the test procedure or the test cassette itself. The test result may be unreliable, and the patient may need to be tested again with a fresh test kit.
-
Partial Test: In some cases, a faint control band may appear. This could suggest an error in sample collection or improper storage of the test kit. A new test may be necessary to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
While often overlooked, the control band is the cornerstone of the rapid strep test. Its presence ensures reliability, while its absence or faint appearance signals the need for further investigation. Understanding the role of the control band empowers healthcare professionals to interpret test results with confidence, leading to accurate diagnoses and effective treatment.
Entities Involved in Rapid Strep Testing
Healthcare Professionals
Physicians are the primary healthcare providers who administer and interpret rapid strep tests. They examine patients, order the test, and analyze the results to determine the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria, the causative agent of strep throat.
Nurses assist physicians by collecting specimen swabs from the patient’s tonsils or throat. They ensure that the specimen is collected properly to yield accurate test results.
Test Components
The rapid strep test kit consists of several components:
- Specimen swab: A sterile swab used to collect a sample from the patient’s throat or tonsils.
- Extraction reagent: A solution that prepares the specimen for testing.
- Test strip: A disposable device that displays the test results. It contains antibodies that react with strep bacteria, leading to the formation of colored bands.
- Control band (C): A reference band that indicates the test is working properly.
Interpreting Results
Positive (+) band: If a colored band appears adjacent to the positive marking on the test strip, it indicates the presence of strep bacteria and a presumptive diagnosis of strep throat. This result typically prompts further evaluation and treatment.
Negative (-) band: If a colored band appears adjacent to the negative marking, it indicates that strep bacteria were not detected, and strep throat is unlikely. However, a negative result may not always rule out strep infection, and further testing may be necessary.
Indirect Entities
Laboratories may play a role in verifying rapid strep test results. In cases where the test result is ambiguous or the clinical presentation suggests a high probability of strep throat despite a negative rapid test, a laboratory culture may be performed for confirmation.
Manufacturers of rapid strep test kits ensure the accuracy and reliability of these essential diagnostic tools. They conduct rigorous testing and adhere to quality standards to provide healthcare professionals with trustworthy results.
Unveiling the Rapid Strep Test: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Essential Entities
Rapid strep test, a common diagnostic tool, plays a crucial role in the detection of Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria responsible for strep throat. Understanding the entities involved in this test is vital for healthcare professionals and patients alike. This blog post delves into the entities involved in the rapid strep test, categorizing them based on their level of direct and indirect involvement.
Entities Directly Involved
Healthcare Professionals: The Gatekeepers of Accuracy
- Physicians: These highly trained individuals are responsible for administering the test, interpreting the results, and providing appropriate treatment recommendations. Their expertise ensures the test’s accuracy and reliability.
- Nurses: As the hands-on assistants, nurses play a vital role in collecting the specimen, which requires skill and care to obtain a suitable sample for testing.
The Test Kit: Unraveling Its Components
- Rapid strep test kit: This essential tool comprises several components, including the specimen swab, extraction reagent, test strip, and control band (C). Each component contributes to preparing, processing, and displaying the test results.
Test Results: Interpreting the Bands
- Positive (+) band: A visible band indicates a positive result, suggesting the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes. This calls for prompt antibiotic treatment to prevent complications.
- Negative (-) band: A single band in this area signifies a negative result, ruling out strep throat as the cause of symptoms. Further evaluation may be necessary to determine the underlying issue.
Entities Related to the Test
Tonsillar/Throat Swab: The Key to Sample Collection
- Tonsillar swab/Throat swab: These swabs are specifically designed to collect a sample from the tonsils or back of the throat, where the bacteria responsible for strep throat reside. Correct swab technique is crucial for obtaining an accurate sample.
Tonsilitis: The Condition Under Scrutiny
- Tonsillitis: This condition refers to the inflammation of the tonsils, often caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. Rapid strep test aids in its diagnosis, guiding treatment decisions and preventing potential complications.
Entities Indirectly Involved
Physician Assistants: Extending the Reach of Care
- Physician assistants: Their involvement in the test varies depending on state regulations. However, if authorized, they may assist in test administration and result interpretation, expanding access to strep throat diagnosis.
Laboratory: Verifying the Verdict
- Laboratory: In some cases, the test results may need to be verified by a laboratory. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of the diagnosis, especially when the results are equivocal or inconsistent with the clinical presentation.
Manufacturers: Behind the Scenes of Accuracy
- Manufacturers of rapid strep test kits: Companies such as Abbott Laboratories and Becton Dickinson play a pivotal role in producing and distributing these test kits. Their expertise in diagnostics ensures the test’s quality and reliability.
The rapid strep test is a valuable tool in the diagnosis of strep throat, enabling prompt treatment and preventing complications. By understanding the entities involved in this test, healthcare professionals can effectively use it to guide patient care. From healthcare professionals to test kit manufacturers, each entity contributes to the accuracy, reliability, and impact of this essential diagnostic tool.