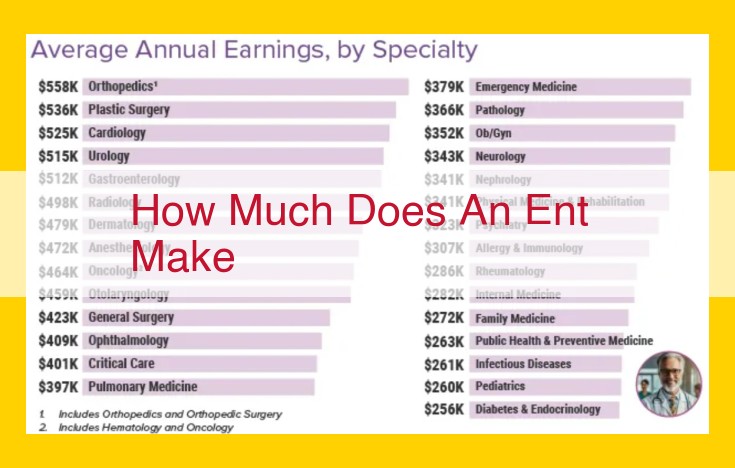
Otolaryngologists (ENTs) diagnose and treat ear, nose, and throat disorders. Their salaries can vary depending on their experience, practice setting, and location. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for otolaryngologists in 2021 was $293,600. Nurse practitioners and physician assistants in otolaryngology can also earn substantial salaries, although their earnings typically fall short of those of physicians.
Medical Professionals and Their Roles in Treating Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders
When dealing with ear, nose, and throat (ENT) issues, consulting the right healthcare professionals can make all the difference. Among these experts, otolaryngologists, also known as ENTs, stand out as the primary specialists. These highly trained physicians have undergone extensive medical education and residency programs specifically focused on the intricate workings of these anatomical regions.
Supporting ENTs in their practice are physician assistants (PAs) and nurse practitioners (NPs). PAs possess a master’s degree in physician assisting and work under the supervision of physicians, performing a wide range of tasks, including diagnosing and treating illnesses, ordering tests, and assisting in surgical procedures. NPs hold a master’s or doctoral degree in nursing, specializing in advanced practice nursing. They provide comprehensive care, including patient assessments, diagnosis, medication management, and health education.
Professional Organizations for ENT Specialists
Beyond individual practitioners, there are several professional organizations dedicated to advancing the field of ENT medicine and providing support to its members. The American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) is a reputable organization that represents over 12,000 otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, and scientists dedicated to improving patient care through education, research, and advocacy.
Another notable organization is the American Society of Pediatric Otolaryngology (ASPO), which focuses specifically on the specialized care of children with ENT conditions. ASPO members play a vital role in advancing research, promoting education, and supporting the unique needs of young patients with ear, nose, and throat disorders.
Professional Organizations in the ENT Field
In the realm of ear, nose, and throat disorders, specialized medical professionals and organizations play a crucial role in providing comprehensive care and advancing knowledge within the field. Among these esteemed institutions, the American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) and the American Society of Pediatric Otolaryngology (ASPO) stand out as beacons of expertise and advocacy.
The AAO-HNS, representing over 12,000 otolaryngologists and other healthcare professionals, serves as the leading organization dedicated to advancing the science and practice of otolaryngology. Through its extensive educational programs, clinical guidelines, and advocacy efforts, the AAO-HNS empowers its members to deliver the highest quality of care to patients with ENT disorders.
Similarly, the ASPO focuses specifically on the specialized needs of children with ear, nose, and throat conditions. Comprised of pediatric otolaryngologists, the ASPO provides invaluable resources and support to its members, fostering collaboration and promoting the well-being of young patients. Together, these organizations play an indispensable role in shaping the future of ENT care and ensuring optimal outcomes for patients across the globe.
The Educational Journey to Otolaryngology: A Path to Healing
The path to becoming an otolaryngologist, a medical professional specializing in disorders of the ear, nose, and throat, is a rigorous and rewarding journey. Aspiring otolaryngologists embark on an extensive educational and training pathway that equips them with the knowledge, skills, and expertise to diagnose and treat a wide range of ear, nose, and throat conditions.
Aspiring otolaryngologists begin their journey by pursuing a Bachelor’s Degree in a Science-Related Field. Common choices include Biology, Chemistry, or Physics. This undergraduate education provides a strong foundation in the sciences, serving as a stepping stone for medical school.
Next, they progress to Medical School, where they engage in rigorous academic study and clinical rotations. During medical school, they gain a comprehensive understanding of human anatomy, physiology, and disease processes. They also develop essential clinical skills through hands-on experiences in various medical settings.
Upon graduating medical school, aspiring otolaryngologists enter Otolaryngology Residency Programs. These highly competitive programs provide specialized training in the diagnosis and management of ear, nose, and throat disorders. Residents rotate through diverse clinical settings, gaining proficiency in surgical procedures, endoscopic examinations, and other advanced techniques.
After completing residency, some otolaryngologists pursue additional training through Fellowship Programs. These specialized programs offer advanced training in specific areas of otolaryngology, such as head and neck surgery, pediatric otolaryngology, or rhinology.
Through this rigorous educational and training pathway, otolaryngologists emerge as highly skilled and knowledgeable medical professionals, dedicated to improving the health and well-being of their patients. Their journey is a testament to their passion for medicine and their commitment to providing exceptional care.
Include information on medical schools, residency programs, and fellowship programs.
Educational and Training Institutions: The Pathway to Otolaryngology Expertise
The path to becoming an otolaryngologist, an esteemed medical professional specializing in the intricate workings of the ears, nose, and throat, is meticulously crafted. It commences with an arduous journey through the hallowed halls of medical school, where aspiring physicians delve into the depths of anatomy, physiology, and disease.
Upon completing medical school, these intrepid individuals embark on a residency program dedicated solely to otolaryngology. This rigorous training, spanning three to five years, provides them with invaluable hands-on experience in diagnosing and treating a myriad of ear, nose, and throat ailments.
For those seeking even greater specialization, the pursuit of a fellowship program beckons. These specialized training endeavors, typically lasting one to two years, equip physicians with advanced expertise in subfields such as otology, rhinology, laryngology, or head and neck surgery. By the culmination of this educational odyssey, these otiatrists emerge as highly skilled and knowledgeable purveyors of exceptional ear, nose, and throat care.
The Role of CMS in Shaping Otolaryngology Payment Policies
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), a federal agency, plays a critical role in the healthcare industry, including in the field of otolaryngology. CMS is responsible for establishing payment policies for services provided under Medicare and Medicaid, which are the primary health insurance programs for the elderly, disabled, and low-income Americans.
One of CMS’s key responsibilities is to determine how much Medicare and Medicaid will pay for otolaryngology services, such as ear exams, sinus surgery, and allergy testing. To do this, CMS considers a variety of factors, including the cost of providing the service, the complexity of the procedure, and the patient’s medical needs.
CMS’s payment policies have a significant impact on otolaryngologists and their patients. If CMS sets payment rates too low, otolaryngologists may be less likely to provide certain services, which could limit patients’ access to care. Conversely, if CMS sets payment rates too high, it could lead to increased healthcare costs for taxpayers and beneficiaries.
In addition to setting payment rates, CMS also plays a role in developing quality measures for otolaryngology services. These measures are used to assess the quality of care that patients receive and to identify areas where improvement is needed. CMS uses quality measures to determine how much to pay for services and to make decisions about which providers to include in its network.
CMS’s role in setting payment policies for otolaryngology services is complex and can be controversial. However, CMS’s goal is to ensure that Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries have access to high-quality, affordable healthcare. By considering the needs of patients, providers, and taxpayers, CMS can develop payment policies that achieve this goal.
The Vital Role of BLS in Tracking Employment and Salary Data for Otolaryngologists
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) serves as a crucial source of information for understanding the evolving employment landscape and compensation trends within various industries, including healthcare. For otolaryngologists, the BLS plays a pivotal role in monitoring their workforce dynamics and providing valuable insights.
One of the key functions of the BLS is to gather and analyze employment data. This includes tracking the number of otolaryngologists actively employed in the United States, as well as their distribution across different regions and sectors. This information helps policymakers, researchers, and healthcare organizations make informed decisions about workforce planning and resource allocation.
Furthermore, the BLS collects and disseminates salary data for otolaryngologists. Through its Occupational Employment Statistics (OES) program, the BLS provides detailed information on median annual salaries, as well as the range of salaries earned by otolaryngologists in different geographic areas and practice settings. This data is essential for healthcare professionals in making informed career decisions and negotiating competitive compensation packages.
The BLS also tracks employment trends over time, allowing us to observe how the otolaryngology workforce is changing. This information can provide insights into factors affecting employment growth, such as advancements in medical technology, changes in healthcare policies, and the aging population. It also helps identify emerging trends and areas of growth within the field.
By providing comprehensive employment and salary data, the BLS empowers otolaryngologists, healthcare organizations, and policymakers with the information they need to make informed decisions. This data contributes to the efficient functioning of the healthcare system and ensures that otolaryngologists are adequately compensated for their vital contributions to patient care.
Introduce the American Tinnitus Association and Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA) as organizations dedicated to providing support and resources to individuals with ear-related conditions.
Advocacy Organizations and Resources
Supporting Individuals with Ear Conditions
In the realm of hearing health, two remarkable organizations stand tall: The American Tinnitus Association and The Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA). These entities are dedicated to providing unwavering support and essential resources to individuals navigating various ear-related conditions.
The American Tinnitus Association is a beacon of hope for those impacted by the persistent ringing or buzzing in their ears, known as tinnitus. This organization understands the challenges that accompany this condition, offering a lifeline of empathy and support. Their comprehensive website and array of resources, including educational materials, connection with support groups, and the latest research, empower individuals to manage their symptoms effectively.
HLAA, on the other hand, serves as a vital advocate for individuals with hearing loss. Its mission encompasses connecting, educating, and supporting those navigating the complexities of hearing impairment. Through local chapters and online platforms, HLAA fosters a sense of community, providing a space for individuals to share experiences, access reliable information, and advocate for their needs.
Empowering and Educating
Both organizations recognize the importance of knowledge and empowerment in the journey of ear-related conditions. The American Tinnitus Association tirelessly educates the public about tinnitus, its causes, and treatment options. HLAA, likewise, dedicates itself to dispelling myths and biases surrounding hearing loss, ensuring that individuals have access to the understanding they need to advocate for their health.
A Shoulder to Lean On
These organizations are more than mere providers of information. They are compassionate companions, offering a listening ear and a comforting hand to individuals grappling with the challenges of ear conditions. Support groups, online forums, and telephone helplines create a safe space where individuals can connect with others who truly understand their experiences.
By providing support, resources, and advocacy, the American Tinnitus Association and the Hearing Loss Association of America empower individuals with ear conditions to live their lives to the fullest. Their unwavering commitment to the well-being of those they serve is a testament to the power of collective action and the transformative impact of compassionate care.
Advocacy Organizations and Resources
In the world of ear health, there are organizations that champion the cause of those affected by ear-related conditions. Two prominent examples are the American Tinnitus Association (ATA) and the Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA).
ATA: A Voice for Those with Ringing Ears
For those who suffer from the constant torment of tinnitus, the ATA serves as a beacon of hope and support. This organization relentlessly advocates for increased research, improved treatment options, and a greater understanding of this enigmatic condition. Through its educational programs and advocacy efforts, the ATA empowers individuals to manage their tinnitus and live fulfilling lives.
HLAA: Empowering the Hearing Impaired
The HLAA stands tall as the leading advocate for those living with hearing loss. This organization provides an invaluable lifeline of support, information, and resources to help individuals navigate the challenges of hearing impairment. HLAA’s advocacy work focuses on improving communication accessibility, advocating for fair employment practices, and ensuring the availability of assistive technology.
By uniting affected individuals, raising awareness, and influencing policy, these organizations play a crucial role in improving the well-being of those living with ear-related conditions.