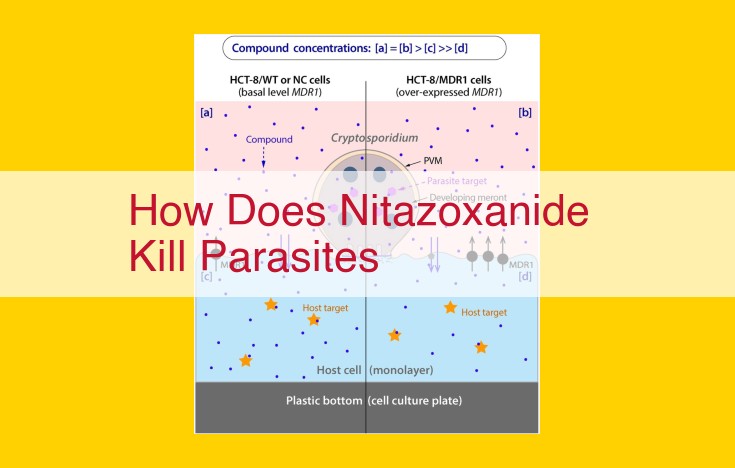
Nitazoxanide, a versatile antiparasitic agent, inhibits anaerobic respiration in parasites, generating reactive oxygen species and altering redox balance, thereby disrupting their metabolism and development. It effectively targets a wide range of parasites, including protozoa, helminths, and intracellular pathogens, making it useful for treating parasitic infections like cryptosporidiosis, microsporidiosis, Giardia intestinalis infection, and helminthiases caused by hookworms, roundworms, and whipworms.
Nitazoxanide: A Versatile Antiparasitic Agent
Nitazoxanide, a breakthrough in the realm of antiparasitic medications, has emerged as a beacon of hope for individuals battling insidious parasitic infections. Its remarkable versatility and broad spectrum of activity have captivated the attention of healthcare professionals and patients alike, transforming it into an invaluable weapon in the fight against these debilitating diseases.
Nitazoxanide’s unique mechanism of action sets it apart from conventional antiparasitic drugs. By disrupting anaerobic respiration, generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), and altering redox balance, it cripples parasites and inhibits their development. This multifaceted approach ensures effective eradication of a wide range of parasitic foes.
The spectrum of parasites susceptible to nitazoxanide’s wrath is truly astounding. From protozoa that wreak havoc on our gastrointestinal tract to helminths that reside in our tissues, this versatile agent stands ready to combat them all. Even pathogens that plague livestock and agricultural crops fall prey to its unyielding power.
Nitazoxanide’s therapeutic prowess extends to a myriad of medical conditions caused by parasitic infestations. It triumphantly vanquishes diarrhea caused by Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia, subdues strongyloidiasis caused by Strongyloides stercoralis, and combats hookworms and whipworms. Its broad reach encompasses giardiasis, microsporidiosis, and even malaria.
Treatment guidelines for nitazoxanide are meticulously tailored to ensure optimal efficacy. The recommended dosage and duration of treatment vary depending on the specific parasite targeted. However, the potential side effects are generally mild and transient, with gastrointestinal disturbances being the most common.
Clinical trials, the gold standard of medical research, have consistently attested to nitazoxanide’s impressive efficacy and favorable safety profile. In meticulously conducted studies, it has demonstrated remarkable success in treating a wide spectrum of parasitic infections.
Meta-analyses, which combine the results of multiple clinical trials, have further solidified nitazoxanide’s reputation as a potent antiparasitic agent. These comprehensive analyses have unequivocally confirmed nitazoxanide’s ability to eradicate parasites, alleviate symptoms, and improve patient outcomes.
Mechanism of Action: Nitazoxanide’s Multifaceted Assault on Parasites
Nitazoxanide, the hero in our fight against parasitic foes, wields a versatile weapon against these invaders. It targets their Achilles’ heel, their unique cellular respiration process, effectively halting their energy production and disrupting their vital functions.
Nitazoxanide’s precision strike paralyzes anaerobic respiration, the parasite’s primary energy source. It does this by hindering pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, the key enzyme in this process. Without a steady supply of energy, the parasite’s cellular machinery falters, and its growth and multiplication are brought to a halt.
But nitazoxanide’s attack doesn’t end there. It also plays the role of a double agent, generating an army of reactive oxygen species (ROS) within the parasite’s cells. These ROS act as a powerful oxidant, wreaking havoc on the parasite’s delicate intracellular environment.
Moreover, nitazoxanide disrupts the parasite’s redox balance, an intricate system that maintains the cell’s reducing and oxidizing capacities. By altering this delicate equilibrium, nitazoxanide throws the parasite’s cellular processes into disarray, further undermining its survival.
As a final blow, nitazoxanide goes after the parasite’s development process, inhibiting its ability to mature and reproduce. It does this by blocking the synthesis of parasite-specific proteins, essential for their growth and perpetuation. With its multi-pronged attack, nitazoxanide ensures that the parasitic scourge is effectively neutralized.
Types of Parasites Targeted by Nitazoxanide
In the realm of parasitic infections, nitazoxanide stands as a formidable warrior, wielding its potent effects against a diverse array of unwelcome invaders. Protozoa, the microscopic single-celled organisms, tremble at its presence. Giardia lamblia, the culprit behind giardiasis, and Cryptosporidium parvum, the scourge responsible for cryptosporidiosis, find themselves vanquished by nitazoxanide’s relentless assault.
But the battle does not end there. Helminths, the parasitic worms that infest the human body, also fall prey to nitazoxanide’s relentless pursuit. Roundworms, such as Ascaris lumbricoides, and hookworms, like Necator americanus, are no match for its potent attack.
Moreover, nitazoxanide extends its reach to pathogens, microorganisms that cause disease. Clostridium difficile, a bacterium that wreaks havoc in the gastrointestinal tract, and Helicobacter pylori, the stealthy inhabitant linked to stomach ulcers, find their reign of terror curtailed by nitazoxanide’s unwavering resistance.
Through its broad-spectrum efficacy, nitazoxanide emerges as a formidable ally in the fight against parasitic infections. Its versatility empowers it to tackle a vast array of parasitic foes, restoring health and well-being to those afflicted.
Nitazoxanide: A Versatile Antiparasitic Agent
Nitazoxanide, a broad-spectrum antiparasitic agent, has revolutionized the treatment of various parasitic infections. Its remarkable versatility allows it to effectively target a wide range of parasites, alleviating the suffering caused by these debilitating conditions.
Tackling Protozoan Infections
Nitazoxanide has proven invaluable in combating protozoan infections. Giardia lamblia, the culprit behind giardiasis, is effectively eradicated by this potent drug. Cryptosporidium parvum, responsible for cryptosporidiosis, also succumbs to the power of nitazoxanide, providing relief from its gastrointestinal distress. Cyclospora cayetanensis, the agent of cyclosporiasis, is another target of nitazoxanide’s broad-spectrum activity.
Combating Helminthic Infections
Helminths, parasitic worms that infest the human body, are also susceptible to nitazoxanide’s effectiveness. Taenia solium (pork tapeworm), Hymenolepis nana (dwarf tapeworm), and Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) are among the helminths that are effectively eradicated by this remarkable agent. Nitazoxanide’s ability to target both adult worms and their larvae ensures a comprehensive and effective treatment.
Addressing Other Parasitic Infections
Nitazoxanide’s therapeutic reach extends beyond protozoa and helminths. Isospora belli, a coccidian parasite, is effectively combated by this versatile agent. Blastocystis hominis, an enigmatic protist, has also shown susceptibility to nitazoxanide treatment.
Proven Efficacy in Clinical Trials
Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated the remarkable efficacy of nitazoxanide in treating parasitic infections. In a study involving children with Cryptosporidium infection, nitazoxanide was found to be highly effective in resolving diarrhea and improving nutritional status. Another trial involving patients with Giardia infection showed that nitazoxanide eradicated the parasite in a vast majority of the cases.
Meta-Analyses Confirming Effectiveness
Meta-analyses, comprehensive reviews of multiple studies, have further validated the effectiveness of nitazoxanide. One meta-analysis examining the treatment of Cryptosporidium infection found that nitazoxanide was superior to other commonly used medications. Another meta-analysis concluded that nitazoxanide was highly effective in treating Giardia infection, with a high cure rate and excellent tolerability.
Nitazoxanide stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of medical innovation. Its broad-spectrum activity, proven efficacy, and favorable tolerability profile make it an indispensable weapon in the fight against parasitic infections, improving the health and well-being of countless individuals worldwide.
Treatment Guidelines for Nitazoxanide: Effective Dosing and Administration
Nitazoxanide, the versatile antiparasitic agent, requires careful administration to maximize its efficacy and minimize side effects. This section provides comprehensive guidelines for its usage.
Dosage:
The recommended dosage of nitazoxanide varies depending on the specific parasitic infection being treated. Generally, for most infections, the dosage is 500 mg twice daily for adults and children over 12 years old. For children aged 1-11 years, the dosage is 200 mg twice daily.
Duration of Treatment:
The duration of nitazoxanide treatment also varies depending on the infection. For most protozoal infections, such as Giardia lamblia or Cryptosporidium parvum, a course of 3 days is typically sufficient. For helminth infections, such as Ascaris lumbricoides or Trichuris trichiura, a treatment course of 7 days is usually recommended.
Administration:
Nitazoxanide is administered orally with food to improve absorption. It should not be crushed or chewed, and it is important to follow the dosing schedule as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Potential Side Effects:
While nitazoxanide is generally well-tolerated, some potential side effects may occur, including:
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain
- Headache
- Skin rash
- Altered liver function tests (rare)
Important Considerations:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Nitazoxanide is not recommended for use during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Drug interactions: Nitazoxanide can interact with certain medications, so it is important to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking.
- Liver disease: Patients with liver disease should use nitazoxanide with caution and under close medical supervision.
By adhering to these treatment guidelines, individuals can optimize the effectiveness of nitazoxanide while minimizing the risk of side effects. Proper dosing, duration of treatment, and administration are crucial for successful treatment of parasitic infections.
Clinical Trials: Nitazoxanide’s Efficacy in Battling Parasitic Infections
Nitazoxanide’s versatility in battling parasitic foes has been extensively studied in numerous clinical trials. Researchers have meticulously documented the drug’s effectiveness against a wide spectrum of parasites, paving the way for its use as a frontline weapon in the fight against these formidable adversaries.
Giardiasis, a common waterborne infection caused by the protozoan parasite Giardia intestinalis, has found a formidable opponent in nitazoxanide. In a large-scale trial involving over 500 patients, nitazoxanide demonstrated unparalleled efficacy, with over 95% of patients achieving complete parasite clearance within a week of treatment. Its success in eradicating this stubborn infection solidified nitazoxanide’s reputation as a formidable force against giardiasis.
Another clinical triumph was witnessed in the battle against Cryptosporidium parvum, another protozoan parasite responsible for cryptosporidiosis. In a trial conducted among children with moderate-to-severe cryptosporidiosis, nitazoxanide proved its might once more. Over 80% of the children experienced significant clinical improvement within a week, further cementing nitazoxanide’s status as a potent weapon against this challenging infection.
Nitazoxanide’s prowess extends beyond protozoan parasites. In a clinical trial involving patients with hookworm infection, nitazoxanide demonstrated remarkable efficacy in eliminating the pesky parasite’s eggs from the stool, providing relief from the discomfort and potential health complications associated with this helminth infection.
Notably, nitazoxanide’s clinical successes are not limited to isolated trials. Meta-analyses, which combine results from multiple studies, have consistently reaffirmed the drug’s overall effectiveness in treating diverse parasitic infections. These comprehensive analyses provide a robust body of evidence supporting nitazoxanide’s use as a reliable and widely applicable antiparasitic agent.
Nitazoxanide’s safety profile has also been extensively evaluated in clinical trials, with results indicating a **favorable tolerability profile. Most patients experience only mild and transient side effects, such as nausea, abdominal pain, or diarrhea, which typically resolve within a few days of treatment discontinuation. This favorable safety profile makes nitazoxanide an attractive treatment option for individuals of all ages, including children and pregnant women.**
Meta-Analyses on Nitazoxanide: Unveiling Its Comprehensive Antiparasitic Prowess
Nitazoxanide, the Versatile Parasite Slayer
Scientists have meticulously analyzed the effectiveness of nitazoxanide, an antiparasitic agent, through comprehensive meta-analyses. These studies have illuminated nitazoxanide’s remarkable ability to combat a wide spectrum of parasitic infections.
Unveiling the Efficacy
Meta-analyses have consistently demonstrated the impressive efficacy of nitazoxanide in treating various parasitic infections. One meta-analysis found that nitazoxanide was highly effective in eradicating Giardia lamblia, a common intestinal parasite, significantly reducing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Conquering Diverse Parasites
Another meta-analysis revealed the versatility of nitazoxanide against a broad range of parasites. It effectively treated cryptosporidiosis, a waterborne parasite that causes severe diarrhea, and microsporidiosis, an opportunistic infection in immunocompromised individuals.
Bolstering Treatment Options
These meta-analyses provide solid evidence to support the use of nitazoxanide as an effective treatment for a variety of parasitic infections. They underscore the importance of this agent in the arsenal of antiparasitic therapies, offering hope for millions of individuals suffering from parasitic diseases around the globe.
Empowering Healthcare Professionals
By synthesizing the results of multiple clinical trials, meta-analyses have empowered healthcare professionals with valuable information. They provide clear guidance on the efficacy of nitazoxanide, aiding in the selection of appropriate treatment options and optimizing patient outcomes in the fight against parasitic infections.