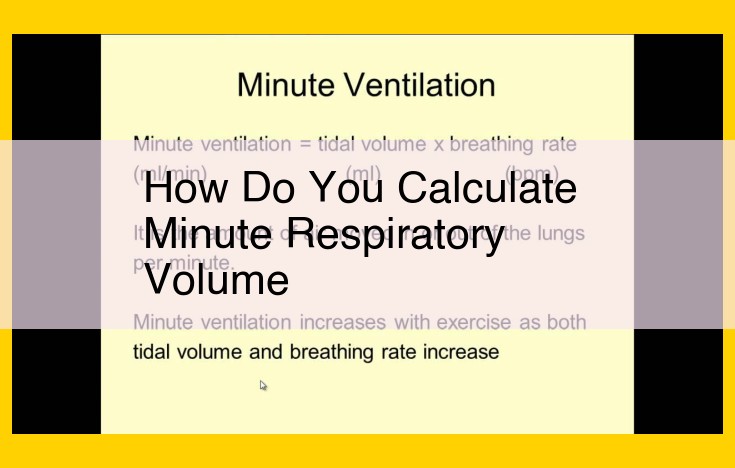
Minute respiratory volume, a measure of ventilation, is calculated by multiplying tidal volume (the volume of air inhaled or exhaled with each breath) by respiratory rate (the number of breaths per minute). This calculation determines the total volume of air moved in and out of the lungs per minute. Understanding minute respiratory volume helps assess overall lung function, as it reflects the body’s ability to exchange gases, supply oxygen to tissues, and remove carbon dioxide.
Tidal Volume (VT): The Breath of Life
In the symphony of life, every breath we take is a vital note, carrying a symphony of gases that sustain our existence. Tidal Volume (VT) is the quintessential measure of this respiratory rhythm, representing the volume of air we inhale or exhale during a single breath.
While seemingly effortless, breathing involves a delicate interplay of muscles, organs, and gases. As we inhale, our diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, expanding the chest cavity and drawing air into our lungs. The air, laden with life-giving oxygen, fills the alveoli, tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs.
During exhalation, the process reverses. The diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, reducing the chest cavity’s volume and expelling the air. This air, now depleted of oxygen and carrying the waste product carbon dioxide, is expelled through our airways.
Tidal Volume, therefore, is a fundamental measure of respiratory function, providing insights into the efficiency of our gas exchange and the overall health of our respiratory system. By understanding the intricacies of VT, we unravel the secrets of our breath, the essence of our existence.
Respiratory Rate: The Rhythm of Your Breath
Imagine your lungs as two powerful bellows, rhythmically expanding and contracting to orchestrate the life-sustaining dance of gases. The rate at which these bellows rise and fall is known as respiratory rate, a crucial indicator of your overall health and well-being.
Every minute, your body requires a precise amount of oxygen to fuel its vital processes. The respiratory rate ensures that the lungs deliver this precious gas efficiently. When you inhale, your lungs expand, drawing in fresh air. As you exhale, they contract, expelling carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism.
The average respiratory rate for adults at rest ranges from 12 to 18 breaths per minute. Deviations from this range can signal underlying health issues. A slower than normal rate (bradynea) can indicate respiratory depression, while a rate faster than normal (tachypnea) may suggest stress, anxiety, or respiratory distress.
Monitoring your respiratory rate can be a valuable tool for self-assessment. If you notice significant changes in your breathing rhythm, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Early detection and treatment of respiratory conditions can significantly improve outcomes.
Remember, your respiratory rate is a symphony of life, a testament to the delicate balance your body maintains to sustain you. By understanding and respecting this vital parameter, you empower yourself to take charge of your health and live a life filled with every precious breath.
Ventilation: Process of moving air into and out of the lungs.
Ventilation: The Rhythmic Dance of Life
The human body relies on ventilation, the process of moving air into and out of the lungs, to sustain life. This intricate symphony of inhalation and exhalation ensures an adequate supply of oxygen to the bloodstream, fueling our cells with the energy they need to thrive.
Inhalation: A Symphony of Air Flow
As we inhale, our diaphragm, the muscular dome separating our chest from our abdomen, contracts and flattens. This action creates a vacuum that draws air into the lungs. The rib cage also expands, further increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity, allowing the lungs to expand.
Exhalation: A Gentle Release
When it’s time to exhale, the diaphragm relaxes, returning to its dome shape. The elastic recoil of the lungs and the downward movement of the rib cage then push air out of the lungs and into the atmosphere.
Gas Exchange: A Vital Dance
During both inhalation and exhalation, gas exchange occurs. As air passes through the tiny air sacs in the lungs called alveoli, oxygen from the air diffuses into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide, a byproduct of metabolism, diffuses from the bloodstream into the air sacs to be expelled.
The Rhythmic Cycle
Ventilation is a continuous cycle that repeats approximately 12-15 times per minute. This rhythmic dance of air movement is essential for maintaining the proper balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. Any disruption to this process can lead to respiratory distress and can have serious consequences for our overall health.
Gas Exchange: The Vital Symphony of Life
Amidst the bustling streets and tranquil parks, an intricate dance unfolds within our bodies – gas exchange. This delicate symphony of oxygen and carbon dioxide, performed within the depths of our lungs, sustains every beat of our hearts and fuels our every thought.
As we inhale, a tidal wave of air washes over our lungs, carrying with it a precious cargo of oxygen. Within the alveoli, tiny air sacs that line the lung walls, a wondrous process of exchange takes place. Oxygen, like a benevolent stranger in a crowded room, eagerly crosses the delicate membrane separating our lungs from our bloodstream.
Simultaneously, a chorus of red blood cells, like tireless messengers, crowd into the capillaries that surround the alveoli. Here, they trade their cargo of carbon dioxide, a waste product of our cellular engines, for the life-giving oxygen.
As we exhale, the carbon dioxide-laden air, now a whisper of a memory, is released back into the atmosphere. This rhythmic dance, the inhale and exhale, the exchange of gases, is the symphony that keeps our bodies humming in harmony.
Without gas exchange, our cells would suffocate, starved of the oxygen they need to thrive. Our minds would fade, our muscles would weaken, and our lives would dwindle to a mere flicker. It is in this vital exchange, this intricate symphony of life, that we find the true essence of our being.
Spirometry: A Non-Invasive Window into Lung Function
Spirometry emerges as a cornerstone of respiratory assessment, providing healthcare professionals with a invaluable tool to measure lung performance and detect breathing abnormalities. This non-invasive test involves having the patient exhale forcefully into a device called a spirometer. By analyzing the volume and flow of air during forced exhalation, spirometry helps us understand the intricacies of lung function.
During spirometry, the patient sits comfortably and inhales deeply. They’re then instructed to exhale as forcefully and quickly as possible through a mouthpiece connected to the spirometer. The device records a graph of airflow over time, known as a spirogram, which provides key measures of lung function.
Key Parameters Measured by Spirometry:
- Tidal Volume (VT): The volume of air inhaled or exhaled in a single breath.
- Respiratory Rate (f): The number of breaths per minute.
- Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 Second (FEV1): The volume of air exhaled in the first second of forced exhalation.
- Forced Vital Capacity (FVC): The total volume of air exhaled with maximum effort.
Spirometry is widely used to diagnose and monitor respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cystic fibrosis. By comparing a patient’s results to established norms, healthcare professionals can assess lung function and identify potential breathing impairments. Early detection and appropriate management of these conditions can significantly improve patients’ quality of life and overall health.
Pulmonary Function Testing: Unveiling Your Lungs’ Secrets
In the realm of respiratory health, pulmonary function testing plays a pivotal role in uncovering the mysteries hidden within your lungs. This comprehensive suite of tests provides a detailed assessment of your lungs’ capabilities, revealing how efficiently they exchange gases, their capacity, and their overall functioning.
Gas Exchange: The Vital Dance of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Pulmonary function testing measures the rate at which oxygen is inhaled and carbon dioxide is exhaled. This exchange of gases is essential for maintaining a healthy balance within the body. If the exchange is impaired, it can lead to a myriad of respiratory issues.
Spirometry: A Window into Lung Capacity
Spirometry is a non-invasive test that analyzes lung function by measuring the volume and flow of air you exhale into a device called a spirometer. This test reveals crucial information about your lung capacity, the tidal volume (the amount of air inhaled and exhaled in a single breath), and the respiratory rate (the number of breaths per minute).
Additional Pulmonary Function Tests
Beyond spirometry, pulmonary function testing encompasses a range of other tests that provide even more granular insights into lung function:
- Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) measures the maximum speed at which you can exhale air.
- Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 Second (FEV1) gauges the amount of air you can forcefully exhale in one second.
- Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) determines the total amount of air you can forcibly exhale after taking the deepest possible breath.
These tests paint a comprehensive picture of your lungs’ health, helping healthcare professionals identify potential respiratory issues, monitor existing conditions, and track the effectiveness of treatment plans.
Unveiling the Importance of Pulmonary Function Testing
Pulmonary function testing is crucial for diagnosing and managing a wide range of respiratory conditions, such as:
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary fibrosis
By understanding your lungs’ capabilities and limitations, pulmonary function testing empowers you and your healthcare team to develop tailored treatment plans that optimize your respiratory health and enhance your overall well-being.
Spirometry: A Vital Tool for Unveiling Lung Function
Spirometry, a non-invasive test, offers a crucial window into the inner workings of our respiratory system. With this remarkable device, we can effortlessly gauge the volume and flow of air that courses through our lungs, providing valuable insights into their overall health.
A Breath of Knowledge
Spirometry, often performed in the comfort of a doctor’s office, requires you to don a mouthpiece and exhale with all your might into a specialized instrument. As your breath fills the spirometer, it meticulously measures the volume of air you expel in a single breath, known as tidal volume. It also keeps a keen eye on the respiratory rate, or number of breaths you take each minute.
Beyond the Numbers
The spirometer’s capabilities extend beyond mere measurements. Through its intricate calculations, it unveils a world of respiratory parameters. It assesses your ventilation, the vital process that ferries air in and out of your lungs, ensuring the essential gas exchange between your body and the surrounding environment. This exchange, the lifeline of your metabolism, involves the intake of life-giving oxygen and the expulsion of waste carbon dioxide.
Unveiling Respiratory Health
Spirometry has proven to be an invaluable tool in the detection and management of a wide spectrum of respiratory ailments, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cystic fibrosis. Deviations from normal spirometry results can prompt further investigations, guiding physicians toward an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Empowering Patients
For individuals with respiratory conditions, spirometry offers a potent tool for self-monitoring and management. Regular tests provide a tangible measure of lung function, empowering patients to actively participate in their healthcare decisions. By tracking their spirometry results over time, they can identify potential flare-ups and adjust medications accordingly, promoting optimal respiratory health.
Pneumotachograph: Unveiling the Flow of Breath
In the intricate symphony of respiration, where air ebbs and flows like a rhythmic tide, the pneumotachograph emerges as a meticulous instrument that deciphers the intricacies of this vital process. This remarkable device, with its intricate sensors, meticulously measures the volume and velocity of air coursing through the respiratory system with unmatched precision.
The pneumotachograph’s genesis lies in the need to quantify the intricate interplay of gases within the lungs. By carefully calibrating its sensitive components, researchers and clinicians can glean invaluable insights into the pulmonary health of individuals. The device’s design features a delicate diaphragm, a thin membrane that gently partitions the respiratory circuit. As breath traverses this diaphragm, it induces a subtle pressure gradient that is meticulously measured by the pneumotachograph’s sensors.
The data gathered by the pneumotachograph unlocks a wealth of information about respiratory function. It can accurately determine the tidal volume, the volume of air inhaled and exhaled with each breath, providing a crucial indicator of the lungs’ capacity. Additionally, the pneumotachograph can precisely gauge the respiratory rate, the cadence of breaths per minute, revealing any abnormalities in the rhythm of respiration.
Beyond these fundamental parameters, the pneumotachograph unveils a deeper understanding of gas exchange, the delicate dance between oxygen and carbon dioxide within the lungs. By meticulously tracking the flow of these gases, researchers and clinicians can assess the lungs’ efficiency in delivering life-sustaining oxygen to the bloodstream while concurrently expunging the metabolic byproduct, carbon dioxide.
In clinical settings, the pneumotachograph plays a pivotal role in evaluating respiratory disorders, guiding therapeutic interventions with accuracy. Its ability to pinpoint flow abnormalities aids in diagnosing and managing conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and restrictive lung diseases. The device’s real-time monitoring capabilities prove invaluable in critical care settings, ensuring optimal respiratory support for patients in delicate states.
As a guardian of respiratory health, the pneumotachograph empowers medical professionals with a detailed understanding of the intricate choreography of breath. Its meticulous measurements guide diagnoses, shape treatment strategies, and ultimately safeguard the well-being of individuals, ensuring that the symphony of respiration continues to serenade life with its steady rhythm.
Capnography: Unveiling the Secrets of Exhaled Carbon Dioxide
In the realm of respiratory monitoring, capnography stands out as an invaluable tool. This device unlocks the mysteries of exhaled carbon dioxide, revealing critical insights into our lung function and health status.
Imagine a breathalyzer, but instead of alcohol, it analyzes the concentration of carbon dioxide in your breath. As we exhale, our lungs release carbon dioxide, a byproduct of our body’s metabolic processes. By meticulously measuring the levels of this gas in our exhaled air, capnography provides invaluable information about our respiratory health.
Capnography’s prowess lies in its ability to continuously monitor carbon dioxide levels. This real-time data allows healthcare professionals to track changes in our breathing patterns and respond promptly to any abnormalities.
Capnography plays a crucial role in various clinical settings, including:
- Intensive Care Units (ICUs): Monitoring patients on ventilators or experiencing respiratory distress
- Operating Rooms: Ensuring adequate ventilation during surgery
- Emergency Departments: Evaluating patients with breathing difficulties
Benefits of Capnography
The benefits of capnography extend far beyond its accuracy and versatility. It offers:
- Early detection of respiratory problems: By swiftly identifying subtle changes in carbon dioxide levels, capnography can alert clinicians to potential respiratory complications before they become serious.
- Assessment of ventilation effectiveness: Capnography helps evaluate how well a ventilator or other respiratory support device is assisting the patient’s breathing.
- Metabolic monitoring: Capnography provides insights into the patient’s metabolic rate, aiding in the management of conditions like sepsis and shock.
Capnography: A Lifeline in Respiratory Care
Capnography has revolutionized respiratory monitoring, providing an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals. Its ability to accurately measure carbon dioxide levels and monitor respiratory function has significantly improved patient outcomes and enhanced the safety of surgical and critical care procedures.
As we continue to delve into the intricacies of respiratory physiology, capnography remains a cornerstone of respiratory assessment, ensuring the well-being of those we care for.
Respiratory Physiology: A Journey into Breathing
In the realm of human physiology, respiration stands as a vital process that sustains our every breath. It’s a delicate dance between our lungs and the surrounding air, ensuring the life-sustaining exchange of gases.
Tidal Volume and Respiratory Rate: The Rhythm of Breathing
Every inhalation and exhalation paints a rhythmic tapestry known as tidal breathing. The volume of air exchanged with each breath is tidal volume, while the respiratory rate measures the frequency of these breaths per minute.
Ventilation and Gas Exchange: The Gateway to Life
Ventilation is the process of moving air in and out of the lungs, akin to a gentle bellows. Within the lungs, a remarkable exchange takes place: gas exchange. Oxygen, essential for cellular respiration, diffuses into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide, a byproduct of metabolism, is exhaled.
Respiratory Assessment: Uncovering the Secrets of Breathing
To unravel the mysteries of respiration, a range of assessment techniques beckon:
- Spirometry: A non-invasive test that measures lung capacity and airflow.
- Pulmonary function testing: An array of tests that delve into various aspects of lung function.
Spirometers and Pneumotachographs: Instruments of Discovery
Spirometers are like miniature respiratory detectives, capturing the volume and flow of air during breathing. Pneumotachographs, with their uncanny precision, measure the flow of air in real-time.
Oxygen Consumption: The Fuel for Life
Oxygen consumption drives the engine of human metabolism, providing the fuel for energy production. Every breath we take is a testament to the vital role oxygen plays in sustaining our existence.
Carbon dioxide, the inevitable byproduct of metabolism, is also an indicator of respiratory health. Its concentration in exhaled air, measured by capnographs, offers a glimpse into the body’s metabolic processes.
Understanding the intricate symphony of respiration is paramount for maintaining healthy lungs and a vibrant life. By exploring the concepts and techniques outlined in this article, we embark on a journey to appreciate the remarkable mechanics that sustain every breath we take.
Respiratory Physiology and its Impact on Metabolism
Our bodies rely on the intricate workings of our respiratory system to maintain a healthy equilibrium. This system plays a crucial role in gas exchange, ensuring a steady supply of oxygen to every cell while eliminating the waste product of metabolism – carbon dioxide.
Respiratory Physiology: The Basics
Each breath we take involves a complex interplay of processes. Tidal volume, the amount of air inhaled or exhaled in a single breath, works in tandem with respiratory rate, the number of breaths per minute, to facilitate ventilation, the movement of air in and out of the lungs. These processes culminate in gas exchange, the transfer of oxygen from the lungs into the bloodstream and the release of carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the lungs.
Respiratory Assessment Techniques: Uncovering Lung Function
Assessing lung function is essential for diagnosing and managing respiratory conditions. Spirometry, a non-invasive test, measures the volume and flow of air moved in and out of the lungs. Pulmonary function testing, a more comprehensive series of tests, provides a detailed evaluation of various aspects of lung function. These tests utilize devices such as spirometers, pneumotachographs, and capnographs to monitor airflow, pressure, and carbon dioxide levels.
Respiratory Factors Affecting Metabolism
The respiratory system’s role extends beyond gas exchange. It also influences our metabolism, the body’s energy production process. Oxygen consumption, the rate at which the body utilizes oxygen for energy, is a fundamental measure of metabolic activity. Conversely, carbon dioxide production, the rate at which the body releases carbon dioxide as a byproduct of metabolism, reflects the body’s energy expenditure.
Carbon Dioxide Production: A Window into Metabolic Rate
Carbon dioxide production serves as a valuable indicator of metabolic rate. Increased levels of carbon dioxide indicate a higher metabolic rate, suggesting increased energy expenditure. This information is particularly useful in assessing the effectiveness of exercise programs or nutritional interventions designed to modify metabolic function.
Understanding the intricate relationship between respiratory physiology and metabolism empowers us to make informed choices that optimize our health and well-being. By monitoring respiratory function and considering its impact on metabolism, we can strive to maintain a balanced and efficient physiological system.