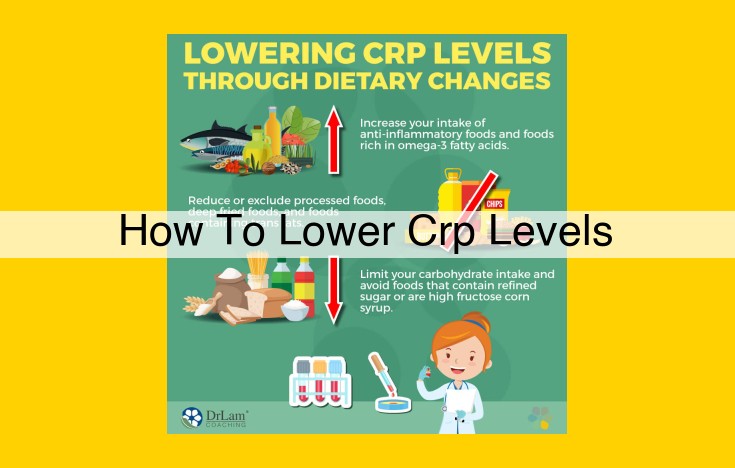
To lower CRP levels, embrace healthy lifestyle factors such as weight loss, exercise, and a Mediterranean diet. Incorporate anti-inflammatory supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin, and fish oil into your routine. Consult your healthcare provider to explore medications like statins or biological therapies if necessary. Regularly monitor CRP levels to track inflammation and heart disease risk, addressing underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome proactively. By adopting these measures, you can effectively reduce inflammation and improve your overall heart health.
Discuss the strong correlation between certain lifestyle factors and cardiovascular health, including weight loss, exercise, and adherence to a Mediterranean diet.
Lifestyle Factors and Cardiovascular Health: A Strong Correlation
A healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy heart. Studies have established a strong correlation between certain lifestyle factors and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
Weight Loss:
Excess weight can put a strain on your heart, increasing the risk of cardiovascular events. Losing weight can reduce stress on the heart, improve blood pressure, and lower cholesterol levels. Aim for a gradual weight loss of 1-2.5 pounds per week through healthy eating and regular exercise.
Exercise:
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood flow, and reduces the risk of blood clots. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Find activities you enjoy, such as brisk walking, swimming, or dancing.
Mediterranean Diet:
The Mediterranean diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, fish, and olive oil. This dietary pattern has been linked to a lower risk of heart disease. The focus on plant-based foods provides antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that protect the heart.
Explain the potential benefits of aspirin and NSAIDs in reducing inflammation and heart disease risk.
Aspirin and NSAIDs: Reducing Inflammation and Heart Disease Risk
In the realm of heart health, inflammation plays a pivotal role. While many factors contribute to inflammation, certain lifestyle choices and medications can offer potent anti-inflammatory benefits, reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. Among these, aspirin and NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) stand out as effective weapons in the fight against inflammation and heart disease.
Aspirin, a widely used drug, has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory properties. It primarily works by inhibiting an enzyme called COX-1, which is involved in the production of prostaglandins, inflammatory mediators that contribute to pain, fever, and inflammation. By blocking COX-1, aspirin effectively reduces the production of these inflammatory molecules, thereby mitigating inflammation throughout the body.
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, also possess potent anti-inflammatory effects. Similar to aspirin, NSAIDs target the COX enzyme, inhibiting both COX-1 and COX-2. COX-2 is particularly involved in inflammation and pain, making NSAIDs especially effective in reducing these symptoms.
Inflammation is strongly linked to the development and progression of cardiovascular disease. By reducing inflammation, aspirin and NSAIDs have been shown to lower the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. Studies have consistently demonstrated that regular use of aspirin or NSAIDs can significantly decrease the risk of these adverse outcomes in individuals with a history of cardiovascular disease or those at high risk.
It’s important to note that aspirin and NSAIDs should be used with caution under medical supervision. While they offer potential benefits in reducing inflammation and heart disease risk, they can also have side effects, such as stomach bleeding and kidney damage. Therefore, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if aspirin or NSAIDs are appropriate for your individual health needs.
In summary, aspirin and NSAIDs provide valuable anti-inflammatory benefits that can help protect against heart disease. By reducing inflammation, these medications contribute to overall cardiovascular health and well-being. However, it’s crucial to use them cautiously and under medical guidance to minimize potential side effects.
Highlight the importance of consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for heart health.
Headline: Fruits, Veggies, and Whole Grains: Your Heart’s Superfoods
The path to a healthy heart starts with what you put on your plate. And when it comes to cardiovascular nourishment, few foods rival the superpowers of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Fruits: A Symphony of Heart-Healthy Nutrients
- Berries, citrus fruits, and apples offer a vibrant canvas of antioxidants that protect against cell damage, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease.
- Potassium, found in bananas and melons, helps regulate blood pressure, easing the workload on your heart.
- Fiber-rich fruits, like raspberries and pears, aid in digestion, reducing LDL cholesterol levels.
Veggies: The Guardians of Heart Health
- Leafy greens like spinach and kale are loaded with lutein, a powerful antioxidant that combats oxidative stress in the heart.
- Tomatoes and bell peppers are excellent sources of vitamin C, essential for collagen production, which strengthens blood vessels.
- Vegetables rich in fiber, such as carrots and broccoli, promote regularity, maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
Whole Grains: The Foundation for a Strong Heart
- Brown rice, quinoa, and oatmeal contain soluble fiber, which binds to and removes bad cholesterol from the bloodstream.
- Whole grains provide complex carbohydrates that stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing insulin spikes that can lead to heart disease.
- B vitamins in whole grains support heart health by reducing homocysteine, a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Incorporating these heart-healthy superfoods into your daily diet is a delicious and effective way to nourish your heart and safeguard your well-being. Embrace the flavors of nature’s pharmacy and give your heart the gift of optimal health today.
The Role of Omega-3s, Curcumin, and Fish Oil in Heart Health
Inflammation plays a crucial role in the development of cardiovascular diseases, making it essential to explore natural remedies that can reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Heart’s Guardian
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and tuna, are well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines, which contribute to plaque formation and blood vessel damage. Studies have shown that increasing omega-3 intake can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Curcumin: A Golden Anti-inflammatory
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, is a powerful anti-inflammatory that has gained attention for its potential role in cardiovascular health. It acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals that can damage heart cells. Curcumin supplementation has been shown to improve blood flow, reduce inflammation, and prevent the development of atherosclerosis.
Fish Oil: A Wellspring of Omega-3s
Fish oil is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, providing both EPA and DHA. These essential fatty acids reduce inflammation, improve blood lipid profiles, and regulate heart rhythm. Regular fish oil consumption is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular events, including sudden cardiac death and heart failure.
Omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin, and fish oil are natural remedies that can effectively reduce inflammation and improve cardiovascular health. By incorporating these nutrients into your diet, you can reduce your risk of developing heart disease and enjoy a healthier, longer life. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider before taking any supplements to ensure their safety and effectiveness for you.
Statins and Biological Therapies: Guardians of Heart Health
In the realm of cardiovascular health, where inflammation reigns supreme as a precursor to heart disease, statins and biological therapies emerge as valiant warriors against high cholesterol, the silent saboteur.
Statins: The Cholesterol-Lowering Crusaders
Statins, the champions of cholesterol reduction, have proven their mettle in mitigating the risk of cardiovascular events. These mighty molecules work tirelessly to inhibit the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver, effectively lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL), the notorious “bad” cholesterol. By reducing LDL levels, statins reduce the accumulation of plaque in arteries, thereby improving blood flow and reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Biological Therapies: Precision Weapons against Inflammation
Biological therapies, the sophisticated soldiers in the war on inflammation, target specific molecules that promote inflammation in the body. These therapies, tailored to inhibit specific inflammatory pathways, have shown promising results in reducing cardiovascular risk. By quelling inflammation, biological therapies combat the underlying culprit that fuels heart disease.
Uniting against the Cholesterol Menace
In the battle against high cholesterol, statins and biological therapies form a formidable alliance. Statins, with their unparalleled ability to lower LDL, lay the groundwork for a healthy cardiovascular system. Biological therapies, with their precision targeting of inflammation, strike at the heart of the problem, further reducing the risk of heart disease.
Personalized Treatment for Optimal Outcomes
Customizing treatment is paramount in harnessing the full potential of statins and biological therapies. Physicians carefully assess each patient’s individual risk factors, lifestyle, and response to medication to tailor a treatment plan designed to maximize cardiovascular health and minimize side effects.
Monitoring and Maintenance: The Key to Success
Regular monitoring is essential to ensure the continued efficacy of treatment. By tracking lipid levels, inflammatory markers, and any potential side effects, physicians can make timely adjustments to the treatment plan, ensuring that patients receive the optimal care. This personalized approach empowers individuals to take active ownership of their heart health, optimizing their chances of a long and healthy life.
Monitor Your Health: C-Reactive Protein (CRP) as a Window into Inflammation
Inflammation: The Silent Enemy
Inflammation plays a crucial role in your body’s response to injuries and infections. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can wreak havoc on your heart health. C-reactive protein (CRP) is a protein released into your bloodstream in response to inflammation. Measuring CRP levels can provide valuable insights into your overall health, particularly your risk of cardiovascular disease.
CRP: A Marker of Heart Health
Research has established a strong correlation between elevated CRP levels and an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular events. High CRP levels indicate the presence of systemic inflammation, which can damage the lining of blood vessels, increase blood pressure, and promote the formation of blood clots.
Monitoring CRP Levels for Prevention
Regular monitoring of CRP levels can help you stay informed about your cardiovascular health. Typical CRP levels range from less than 10 mg/L to over 100 mg/L. Levels above 3 mg/L may indicate the presence of chronic inflammation, while levels over 10 mg/L are considered high risk.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce CRP Levels
Inflammation can be fueled by unhealthy lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and stress. By adopting a healthier lifestyle, you can significantly reduce CRP levels and improve your heart health. Aim for a Mediterranean-style diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fish. Engage in regular physical activity and find healthy ways to manage stress.
Medications and Other Interventions
If lifestyle changes alone do not sufficiently lower your CRP levels, your doctor may prescribe medications or recommend additional interventions. Statins, which lower cholesterol, can also reduce inflammation and CRP levels. Aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be beneficial.
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a valuable indicator of inflammation in your body. Monitoring CRP levels can help you assess your risk of cardiovascular disease and take proactive steps to protect your heart. By embracing a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying health conditions, and consulting with your doctor when necessary, you can keep inflammation under control and maintain optimal heart health.
Discuss the strong link between inflammation and cardiovascular disease.
Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease: The Intimate Connection
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can have serious consequences for our health, especially when it comes to cardiovascular disease.
Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease
Inflammation has been implicated in the development of atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries that can lead to heart attacks and strokes. Inflammatory cells release chemicals that damage the lining of the arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque formation.
Inflammation and Risk Factors
Chronic inflammation is often associated with risk factors for cardiovascular disease, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity. These conditions all promote inflammation, creating a vicious cycle that can damage the heart and blood vessels.
Inflammation and Prevention
The good news is that we can take steps to reduce inflammation and protect our cardiovascular health. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and getting regular exercise can all help to reduce inflammation. Supplements like curcumin and omega-3 fatty acids have also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties.
Inflammation and Heart Health
By understanding the link between inflammation and cardiovascular disease, we can take proactive steps to protect our hearts. Reducing inflammation is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart and preventing serious health complications. Regular checkups, monitoring inflammation markers, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle are essential for managing our cardiovascular risk and ensuring a long and fulfilling life.
**Control the Big Three Health Concerns for a Healthier Heart**
If you want to keep your heart in tip-top shape, you need to pay attention to the big three health concerns that can take a toll on its functionality: cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Cardiovascular disease, which refers to conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, is the leading cause of death worldwide. Factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking increase your risk of developing this deadly disease.
Diabetes, a condition where your body cannot properly use glucose, also poses a significant threat to heart health. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that include obesity, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels, is another major player in cardiovascular health issues. It significantly raises the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
The good news is that by taking control of these three health concerns, you can dramatically reduce your risk of cardiovascular events. Here’s how:
-
For cardiovascular disease, manage your blood pressure, control your cholesterol, quit smoking, and exercise regularly.
-
For diabetes, monitor your blood sugar, take medications as prescribed, and follow a healthy diet and exercise plan.
-
For metabolic syndrome, lose weight, exercise regularly, reduce your intake of sugary drinks, and eat a balanced diet.
By staying vigilant about these three health concerns, you’re taking a proactive step towards protecting your heart. Remember, prevention is always better than cure. So, make healthy choices, consult your doctor regularly, and give your heart the care it deserves.
Managing Health Conditions to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk
Inflammation serves as a silent villain, lurking within the body and wreaking havoc on our cardiovascular health. Chronic inflammation is closely associated with an increased risk of life-threatening cardiovascular events, including heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
However, the good news lies in the power of managing underlying health conditions that fuel this inflammation. By effectively controlling these conditions, we can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular events and safeguard our heart’s well-being.
Cardiovascular Disease: A Battle Against Plaque
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries, narrowing their passageways like congested traffic. This plaque restricts blood flow to the heart, brain, and other vital organs. Managing CVD involves controlling risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, which contribute to plaque formation.
Diabetes: Taming the Sugar Surge
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels. Excess sugar can damage blood vessels and promote inflammation. Managing diabetes involves regulating blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and exercise, thereby reducing the risk of diabetic complications, including cardiovascular disease.
Metabolic Syndrome: A Cluster of Risk Factors
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of several risk factors, including obesity, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. These factors work together to increase the risk of cardiovascular events. Managing metabolic syndrome involves lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss, exercise, and a healthy diet, which can help improve overall cardiovascular health.
By effectively addressing these health conditions, we can quell the underlying inflammation that threatens our cardiovascular well-being. Managing blood pressure, controlling cholesterol levels, regulating blood sugar, and losing weight can significantly reduce the risk of plaque buildup, blood vessel damage, and other heart-related complications. In turn, we empower our hearts with the resilience to thrive for years to come.