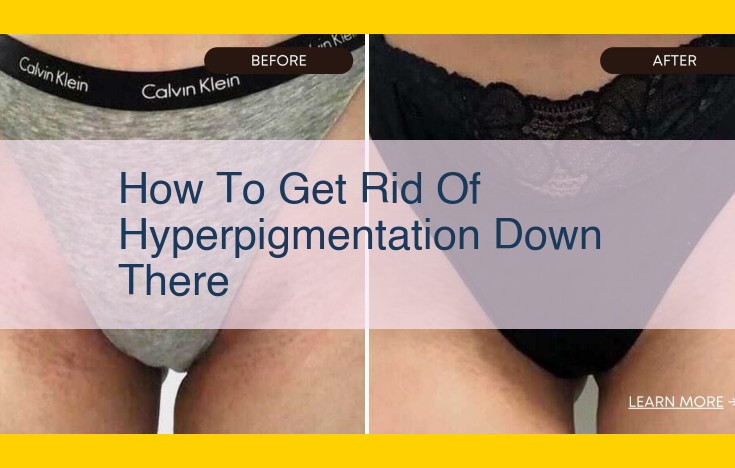
Hyperpigmentation, characterized by darkened areas of skin, can be caused by various factors. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) results from inflammation, melasma from hormonal and environmental influences, sun damage from UV radiation, and hormonal imbalances due to contraceptives, pregnancy, or menopause. Treatment options include topical and oral medications, laser therapy, and chemical peels. Prevention and management involve reducing sun exposure, minimizing inflammation, and addressing underlying health conditions. Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for personalized treatment and effective skincare practices to prevent and manage hyperpigmentation.
- Define hyperpigmentation and its causes.
- Explain the different types of hyperpigmentation.
Understanding Hyperpigmentation: A Comprehensive Guide
Hyperpigmentation, a common skin condition, refers to the darkening of patches of your skin. It occurs when your body produces excess melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Understanding the causes and types of hyperpigmentation can help you effectively manage and treat this condition.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
There are several types of hyperpigmentation, each with its own unique characteristics:
- Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): This type of hyperpigmentation occurs as a result of inflammation, such as from acne, eczema, or injuries. It typically appears as dark patches or spots that fade over time.
- Melasma: Melasma is a condition that causes brown or gray patches on the skin, primarily on the face. It is more common in women and is often triggered by hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or sun exposure.
- Sun Damage: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can damage skin cells and trigger melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation. This type of hyperpigmentation typically appears as freckles, age spots, or sunspots.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Unveiling Its Causes and Triggers
When your skin undergoes inflammation, it may leave behind an unwanted souvenir – post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). This unsightly darkening of the skin occurs due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives our skin, hair, and eyes their color.
The inflammatory process that triggers PIH begins with an injury to the skin. This injury can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Acne: The inflammation caused by acne can lead to the formation of dark spots after the blemishes have healed.
- Eczema: The chronic inflammation associated with eczema can also result in hyperpigmentation, especially in areas where the skin has been scratched or irritated.
- Injuries: Cuts, burns, and other types of injuries can damage the skin’s melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin. As the skin heals, these cells may produce too much melanin, leading to PIH.
Understanding the triggers of PIH is crucial for preventing and managing this skin condition. By avoiding or minimizing exposure to these triggers, you can reduce the risk of developing PIH and maintain an even skin tone.
Understanding Melasma: A Story of Hormonal and Environmental Influences
Melasma, a common skin condition characterized by dark, irregular patches on the face, affects millions of people worldwide. To delve into its complexities, let’s embark on a storytelling journey, exploring the hormonal and environmental factors that play a crucial role in its development.
Melasma primarily affects women, particularly during pregnancy, when hormonal fluctuations, especially an increase in estrogen and progesterone, can trigger an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Estrogen stimulates melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, while progesterone further enhances this process.
However, hormonal influences are not the sole culprits. Melasma’s story is deeply intertwined with environmental factors. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun acts as a catalyst, exacerbating the condition. UV rays penetrate the skin, damaging melanocytes and triggering an increase in melanin production, leading to the formation of darker patches.
The sun’s harmful rays can penetrate the skin’s protective layers, reaching the deeper layers where melanocytes reside. UV rays stimulate these cells to produce excess melanin, which manifests as dark, uneven spots on the skin.
Melasma’s story is a complex tapestry woven with hormonal and environmental threads. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy or hormonal treatment can disrupt the skin’s delicate balance, while excessive sun exposure further amplifies the effects. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective management and prevention of this common skin condition.
The Role of Sun Damage in Hyperpigmentation
曬傷的皮膚會變得《黝黑》,人們常把這種現象歸咎於黑色素,但黑色素的主要目的是《保護》皮膚免受紫外線傷害。當陽光照射皮膚時,會刺激黑色素細胞產生更多的黑色素,沉澱在皮膚上形成色素沉澱,導致《色素不均》。
陽光中的《紫外線》會損害皮膚細胞的《DNA》,導致發炎和細胞損傷。作為一種自我保護機制,皮膚會產生更多的黑色素來吸收紫外線,並保護受損細胞。然而,過度的黑色素沉澱就會導致明顯的色素沉澱和《斑點》。
預防由陽光引起的色素沉澱至關重要。遵循以下建議可以最大程度地《降低》陽光對皮膚的影響:
- 塗抹防曬霜:每天使用廣譜防曬霜,防曬係數(SPF)至少為 30,PA 值至少為 ++++。
- 遮擋陽光:穿戴保護性服飾,例如長袖襯衫、長褲和帽子,以阻擋陽光直射。
- 避免在高峰時段曬太陽:上午 10 點至下午 4 點之間,陽光最強烈,應儘量避免外出。
- 定期檢查皮膚:定期檢查皮膚是否有新的色素沉澱或其他變化,及早發現和治療。
通過遵循這些預防措施,您可以最大程度地降低陽光對皮膚造成的損害,並減少《色素沉澱》的風險。記住, защищать кожу是保護健康和《美麗》的第一步。
Hormonal Imbalances and Hyperpigmentation: Understanding the Connection
Hyperpigmentation, a common skin concern, can be triggered by various factors, including hormonal imbalances. Understanding how hormones affect melanin production can help us unravel the connection between the two.
Estrogen and Progesterone: The Female Hormones
Estrogen and progesterone, key female hormones, play a crucial role in regulating melanin production. When these hormones are balanced, they help maintain an even skin tone. However, hormonal fluctuations can disrupt this balance, leading to hyperpigmentation.
Contraceptive Pills and Hyperpigmentation
Contraceptive pills, often containing synthetic estrogen and progesterone, can alter hormone levels, potentially triggering hyperpigmentation. This is especially common in women with a predisposition to it or a history of melasma.
Pregnancy and Melasma
During pregnancy, elevated levels of estrogen and progesterone can stimulate melanin production, leading to melasma, characterized by dark patches on the face. This condition typically fades after childbirth as hormone levels return to normal.
Menopause and Hyperpigmentation
Menopause brings about hormonal changes that can affect melanin production. Declining estrogen levels can cause hyperpigmentation, particularly in areas exposed to the sun.
Addressing Hormonal Hyperpigmentation
Hormonal hyperpigmentation can be challenging to manage on your own. Seeking professional advice from a dermatologist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. They can assess hormone levels and recommend appropriate solutions, including:
- Topicals with hydroquinone or kojic acid to lighten skin
- Laser therapy to break down excess melanin
- Chemical peels to exfoliate and promote skin renewal
Hormonal imbalances can disrupt melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation. Understanding this connection and seeking timely treatment can help address this common skin concern effectively. By prioritizing skincare and addressing underlying hormonal issues, we can work towards achieving a more even and radiant complexion.
Treatment Options for Hyperpigmentation: Unlocking a Brighter Complexion
Hyperpigmentation, the darkening of skin patches, can be a frustrating skin concern. While there’s no one-size-fits-all solution, understanding the treatment options is crucial for reclaiming your radiant skin.
Topical and Oral Medications: The Power of Science
Topical treatments, such as creams and serums, are the frontline defense against hyperpigmentation. They contain ingredients like hydroquinone, azelaic acid, and kojic acid that inhibit melanin production, gradually lightening the darkened areas.
If topical treatments don’t suffice, oral medications can offer a more potent solution. Tranexamic acid and glutathione are medications that act systemically to reduce melanin production throughout the body.
Laser Therapy and Chemical Peels: Precision Tools for Pigment Correction
Laser therapy uses concentrated beams of light to break down excess melanin pigments. The procedure is highly effective but requires multiple sessions to achieve optimal results.
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, causing the top layers to peel away and revealing brighter, more even-toned skin underneath. Superficial chemical peels are gentler and suitable for milder hyperpigmentation, while deeper peels offer more dramatic results but come with greater downtime.
Non-Invasive Treatments: Gentle Solutions for Sensitive Skin
Microneedling and microdermabrasion are less invasive procedures that stimulate collagen production and promote skin renewal. These treatments can also help fade hyperpigmentation over time.
Consulting with a Dermatologist: The Key to Personalized Care
Navigating the world of hyperpigmentation treatments can be overwhelming. That’s why it’s essential to consult with a board-certified dermatologist. They can assess your skin type, underlying causes, and recommend the most suitable treatment plan for your unique needs.
Remember, patience and consistency are vital when treating hyperpigmentation. Results may not be immediate, but with proper care and adherence to your treatment regimen, you can gradually restore your skin’s natural radiance.
Prevention and Management of Hyperpigmentation
To effectively manage hyperpigmentation, a multifaceted approach that combines lifestyle modifications, sun protection, and targeted treatments is crucial. Here are some key preventive and management strategies:
Reducing Sun Exposure and Using Sunscreen
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a significant trigger for hyperpigmentation. Limit prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours, to minimize UV damage. When outdoors, seek shade and wear protective clothing, including wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses.
Sunscreen is an essential line of defense against UV rays. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and apply it liberally 15-20 minutes before going outside. Reapply every 2 hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
Adopting Anti-Inflammatory Habits
Inflammation is a common factor contributing to hyperpigmentation. Adopt lifestyle habits that minimize inflammation, such as:
- Following a balanced diet: Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats, which can promote inflammation. Instead, opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Managing stress: Chronic stress can trigger inflammation. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Getting adequate sleep: Sleep deprivation can increase inflammation. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Avoiding smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and promotes inflammation, contributing to hyperpigmentation.
Addressing Underlying Medical Conditions
Underlying medical conditions, such as hormonal imbalances, certain medications, or skin disorders, can contribute to hyperpigmentation. If you suspect a medical condition is causing hyperpigmentation, consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
By implementing these preventive and management strategies, you can reduce the risk of developing hyperpigmentation and improve the appearance of existing dark spots. Remember, consistency and patience are key to achieving optimal results.