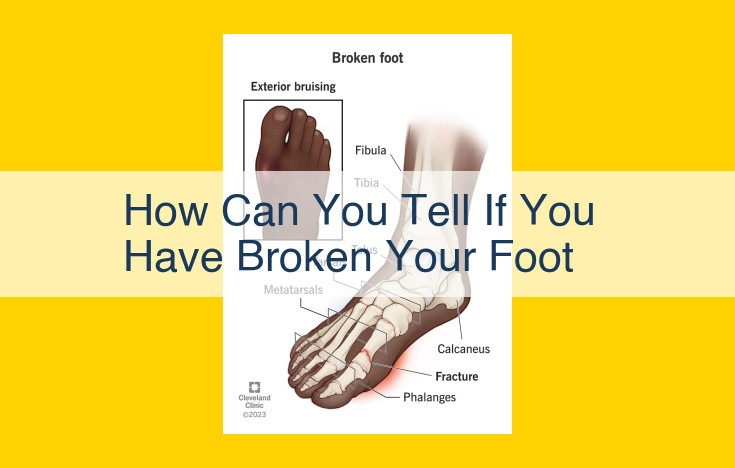
Foot fractures are characterized by severe pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty walking. You may experience numbness or tingling in your toes due to nerve damage. In some cases, bone deformity may be visible. These symptoms can indicate a broken foot, which can be caused by high-impact activities, falls, direct trauma, or stress fractures.
Understanding Foot Fractures: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Foot fractures are a common injury that can occur due to various reasons, such as high-impact activities, accidents, and falls. These injuries can cause significant pain, discomfort, and impaired mobility. Understanding the different types of foot fractures, their common causes, and the symptoms associated with them can help you identify and address the issue promptly.
Symptoms:
- Severe Pain: Foot fractures are often accompanied by intense pain at the site of the injury. The pain may worsen when putting weight on the affected foot or engaging in activities that involve foot movement.
- Swelling: The injured area may become swollen due to inflammation and edema. The swelling can make it difficult to wear shoes or perform daily activities.
- Bruising: Fractured bones can cause blood vessels to rupture, leading to bruising around the affected area. The bruising may appear as a discoloration of the skin.
- Difficulty Walking: Fractures can make walking challenging due to pain and impaired mobility. Fractured bones may not be able to support weight, making it difficult to walk or bear weight on the affected foot.
- Numbness or Tingling in the Toes: In some cases, foot fractures can damage nerves, leading to numbness or tingling in the toes. This is a sign of nerve damage and requires immediate medical attention.
- Bone Deformity: Severe fractures may result in a visible deformity of the bone. This can occur if the fractured bones have shifted or become displaced.
Foot Fractures: A Guide to Symptoms and Causes
Foot fractures are a common ailment that can result from various causes, ranging from high-impact activities to accidents and falls. Understanding the symptoms and causes of foot fractures is essential for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment.
Symptoms: A Tale of Pain and Discomfort
The most prominent symptom of a foot fracture is intense pain, which can vary in severity depending on the location and type of fracture. This pain is often described as sharp, throbbing, or aching. It may worsen with movement and weight-bearing activities.
Swelling is another common symptom, caused by inflammation and fluid accumulation around the injured area. The swelling may make the foot appear larger and disfigured.
Bruising is also common, occurring due to bleeding under the skin. The discoloration can range from mild bruising to extensive hematomas, depending on the severity of the injury.
Difficulty walking is a significant symptom that can severely impact daily activities. Fractures can impair the foot’s ability to bear weight, making walking painful and challenging.
In some cases, nerve damage can occur, leading to numbness or tingling in the toes. This symptom is particularly concerning as it may indicate potential nerve damage.
Bone deformity is another potential symptom, although less common. In severe fractures, the broken bone fragments may shift or deform, resulting in visible abnormalities in the foot’s shape.
Causes of Foot Fractures
Foot fractures, while appearing minor, can significantly impact your mobility and daily life. Understanding the various causes that can lead to these fractures is essential for prevention and proper treatment.
High-Impact Activities
Active individuals who engage in sports, rigorous exercises, or physically demanding occupations are at an increased risk of foot fractures. High-impact activities place tremendous stress on the bones and joints of the foot, especially during landings, jumps, and sudden changes in direction.
Falling
Slips, trips, and falls are common culprits of foot fractures. Falls can result in direct impact on the foot, causing fractures ranging from minor hairline cracks to severe breaks. The severity of the fracture depends on the height of the fall, the surface, and the position in which you land.
Direct Trauma
Direct trauma to the foot can occur from various sources, such as blows, crushing forces, or heavy objects falling on the foot. These injuries are often associated with occupational accidents, construction zones, or sporting events. The force of the impact can cause fractures of varying degrees, from subtle cracks to multiple, displaced fractures.
Stress Fractures
Unlike acute fractures caused by sudden force, stress fractures develop gradually over time due to repetitive stress and overloading. These tiny cracks in the bone occur when the muscles and tendons surrounding the foot cannot absorb the repeated impact, leading to microscopic damage that accumulates into a fracture. Stress fractures are common among athletes, dancers, and individuals who regularly engage in high-intensity physical activities.
Diagnosis: Pinpointing the Source of Foot Discomfort
Physical Examination: Hands-On Assessment
When you visit your doctor, they will meticulously examine your injured foot. Through visual inspection, they will observe any deformity, bruising, or swelling. Then, they will palpate (gently press) the affected area to assess tenderness and pain. Additionally, they will perform movement tests to evaluate your range of motion and identify any instability.
X-rays: Unveiling Hidden Fractures
Diagnose is not complete without advanced imaging technique. X-rays are commonly used to visualize broken bones and determine the type of fracture. These images provide clear insights into the location, severity, and alignment of the damaged bone.
MRI: Soft Tissue Detective
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) takes diagnosis a step further by revealing soft tissue damage. It generates detailed images of ligaments, tendons, and muscles, helping to rule out other potential injuries. MRI is particularly useful for detecting hairline fractures that may not be visible on X-rays.
CT Scan: Precision Imaging for Complex Fractures
In some cases, a computerized tomography (CT) scan may be necessary to obtain detailed cross-sectional images of your foot. CT scans provide high-resolution views of the bones, joints, and soft tissues, making them valuable in diagnosing complex fractures and evaluating the healing process.