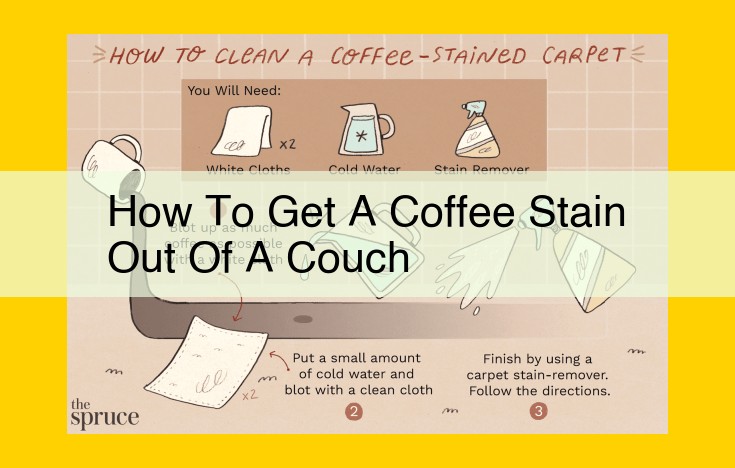
How to Remove a Coffee Stain from a Couch
Coffee stains on a couch can be frustrating, but they can be removed effectively with the right cleaning agents. For fresh stains, blot up excess coffee and apply a mixture of equal parts white vinegar and water. Let it sit for a few minutes, then blot again with a clean cloth. If the stain is older, try using a commercial upholstery cleaner or a baking soda and water paste. Apply the cleaner or paste to the stain, let it sit for 10-15 minutes, and then blot or vacuum it away.
Tackling the Stain Removal Conundrum: A Comprehensive Guide
Stains, those pesky invaders, can strike at any moment, threatening to mar the pristine surfaces of our beloved possessions. From coffee spills on the couch to grass stains on our favorite shirt, removing them can seem like an insurmountable task. But fear not, for this comprehensive guide will empower you with the knowledge and tools to conquer even the most stubborn stains with ease.
Understanding the Challenges of Stain Removal
The key to successful stain removal lies in understanding closeness to topic, the relationship between the stain and the cleaning agent used. Different stains require different cleaning agents based on their chemical composition and the type of fabric or surface they reside on.
Choosing the wrong cleaning agent can exacerbate the stain or even cause permanent damage. For instance, using bleach on a dyed fabric will strip away the color, leaving you with an unsightly discoloration. By evaluating the type of stain and the material it has affected, you can select the most effective cleaning agent that specifically targets and neutralizes its unique properties.
Navigating the Cleaning Agent Spectrum
The vast world of cleaning agents can be daunting, but understanding their varying levels of effectiveness will help you make informed choices. Let’s explore the effectiveness spectrum, from highly related entities to somewhat related entities:
Highly Related Entities
These cleaning agents are like the stain’s kryptonite, specifically formulated to dissolve and remove specific types of stains. For example, using enzyme cleaners to break down protein-based stains like blood or grass, or employing solvents to dissolve greasy stains like oil or paint. These agents are highly effective because they chemically interact with the stain, breaking it down into smaller molecules that can be easily wiped away.
Moderately Related Entities
While not as specialized as highly related entities, these cleaning agents still pack a punch against various types of stains. They include household staples like water, vinegar, baking soda, and dish soap. These agents rely on their solvent or degreasing properties to loosen and dissolve stains. Their versatility makes them a valuable addition to any stain removal arsenal, although they may not be as effective on tough or set-in stains.
Somewhat Related Entities
These cleaning agents are useful in specific situations or for certain types of stains. Hydrogen peroxide can lighten stains on white fabrics, while ammonia can dissolve acidic stains like wine. Vacuum cleaners can remove loose dirt and debris from carpets and upholstery. While not as effective as highly or moderately related entities, these agents can still be helpful when others fail.
Stain removal is not an exact science, but by evaluating closeness to topic and understanding the effectiveness spectrum of cleaning agents, you can significantly increase your chances of success. Remember, different stains require different cleaning approaches. Armed with this knowledge, you can conquer even the most daunting stains and restore the pristine appearance of your belongings. Happy cleaning!
Highly Related Entities: The Secret Weapons for Effective Stain Removal
When it comes to stain removal, there are some game-changing agents that rise to the top as true allies in the battle against stubborn marks. Let’s dive into the most highly related entities, the cleaning agents that target specific stain types and deliver remarkable results.
Coffee Stains on Couch Fabric: Your Go-to Solution
Coffee stains on couch fabric can send shivers down the spine of any homeowner. Fear not, for the savior has arrived! Enzyme cleaners are your secret weapon, as they contain enzymes that break down the proteins in the coffee, making them easy to remove. Simply apply the enzyme cleaner to the stain, let it sit for the recommended time, and wipe away the loosened residue. Voila! Your couch will be stain-free like magic.
Red Wine Stains on Carpet: A Tale of Two Agents
Red wine stains on carpet are another common nemesis. Hydrogen peroxide comes to the rescue with its oxidizing properties, which bleach the stain away. However, always test it on an inconspicuous area first to ensure it doesn’t damage the carpet fibers. For a more delicate touch, white vinegar can also be effective. Its acidic nature breaks down the wine stains, allowing you to blot them away with ease.
Grease Stains on Clothes: The Dish Soap Miracle
Grease stains on clothes are no match for the degreasing power of dish soap. Its surfactant formula breaks down the grease molecules, lifting them from the fabric. Apply a few drops of dish soap directly to the stain, rub it in gently, and let it work its magic before throwing it in the wash. Your clothes will emerge grease-free, ready to conquer any dinner party.
Blood Stains on Sheets: Hydrogen Peroxide, Your Laundry Superhero
Blood stains on sheets can be a nightmare, but hydrogen peroxide is here to save the day. Once again, its oxidizing power comes to the rescue, breaking down the proteins in the blood and removing the stain. Apply a few drops directly to the stain, let it sit for a while, and then wash the sheets as usual. Your sheets will be pristine, without a trace of the nighttime accident.
Moderately Related Entities in Stain Removal: A Practical Approach
When it comes to banishing stubborn stains, knowing which cleaning agents to reach for is crucial. While some stains call for specialized solutions, there are a few moderately effective agents that can handle a wide range of common stains.
Water: The most versatile of them all, water can often dissolve water-based stains like food or drink spills. It’s gentle enough for most fabrics and surfaces, making it a safe first-resort option.
Vinegar: A mild acid, vinegar is effective against stains caused by alkaline substances like bleach or urine. Its acidic nature also helps neutralize odors. For stubborn stains, try diluting it with water.
Baking Soda: A mild alkali, baking soda neutralizes acidic stains like coffee or red wine. It’s also a gentle abrasive that can help lift stains from fabrics. Be careful when using it on delicate materials.
Dish Soap: Formulated to dissolve grease, dish soap can tackle stains from food, cosmetics, and oil. It’s best used for fresh stains and on washable fabrics.
Limitations and Use Cases
While these agents can address many stains, they have limitations:
- Water: Ineffective against greasy or oily stains.
- Vinegar: Can damage some fabrics, so always test it first.
- Baking Soda: Not suitable for delicate fabrics or stains that require bleaching.
- Dish Soap: May not remove all pigments from stains, especially on colored fabrics.
When to Use Them
These moderately effective agents are best used for:
- Fresh stains that haven’t had time to set in.
- Stains on washable fabrics.
- Stains that are not too heavily pigmented.
- Stains that are not caused by bleach or other strong chemicals.
Remember, always test cleaning agents on an inconspicuous area first to ensure they don’t damage the fabric or surface. By understanding the effectiveness and limitations of moderately related entities, you can tackle stain removal with confidence.
Somewhat Related Entities: Cleaning Agents for Specific Circumstances
While moderately related entities offer general-purpose solutions, there are specialized cleaning agents that excel in removing certain types of stains:
-
Hydrogen Peroxide: This disinfectant is potent against coffee and tea stains on light-colored fabrics. Apply it directly to the stain and let it sit for 30 minutes before blotting with a clean cloth.
-
Ammonia: This alkaline solution is ideal for removing bloodstains from clothing. Dilute it with equal parts water and gently dab it onto the stain. Caution: Do not use ammonia on wool or silk fabrics.
-
Enzyme Cleaners: These biological detergents contain enzymes that break down organic matter, making them effective against protein-based stains like grass and blood. Follow the instructions on the product label for the optimal application method.
-
Vacuum Cleaners: A vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter can effectively remove dry stains like dust, pet hair, and pollen from carpets and furniture. Vacuum regularly to prevent embedded dirt and stains.
Remember, when using any cleaning agent, test it on an inconspicuous area of the fabric first to ensure it does not damage the material. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to avoid any adverse effects.