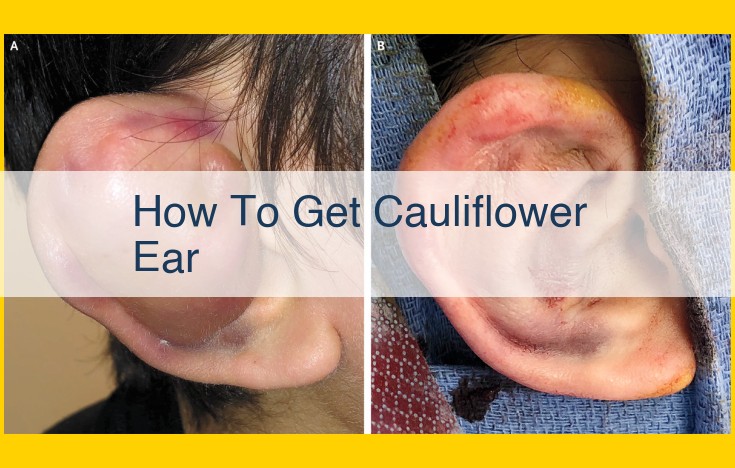
Cauliflower ear is a condition caused by repeated trauma to the ear, usually in contact sports. When the ear is struck, blood vessels rupture and blood collects beneath the skin’s surface. If not drained, this blood can clot and scar, leading to the deformity characteristic of cauliflower ear. Prevention is key, as treatment options are limited and often involve surgery.
Understanding Ear Injuries: Causes and Risk Factors
Ear injuries are a common occurrence, especially among athletes and those who engage in physical activities. Identifying the causes and understanding the risk factors associated with ear injuries is crucial for prevention and timely treatment.
One major cause of ear injuries is traumatic sports injuries. Contact sports such as wrestling, boxing, and football put athletes at risk of sharp blows or impacts to the ear. Accidents, such as falls or collisions, can also result in ear injuries.
Medical procedures, such as ear piercing or ear surgery, can potentially lead to ear injuries if not performed properly or if the aftercare instructions are not followed diligently. Unsterile equipment or poor hygiene practices can increase the risk of infection, which can damage the ear tissues or lead to complications.
Anatomy of the Ear: Unveiling the Intricate Structure
Step into the labyrinthine world of the ear, a sensory marvel that orchestrates our perception of sound.
The auricle, also known as the outer ear, is the visible, shell-shaped structure that gathers sound waves like a satellite dish. Its curved ridges, the concha and pinna, channel these waves toward the ear canal.
Beneath the auricle lies the middle ear, a cavity housing three tiny bones: the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones amplify and transmit sound vibrations from the ear canal to the inner ear.
The inner ear is a complex labyrinth encased within the temporal bone. It comprises the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure lined with sensory hair cells. These cells convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that travel along the auditory nerve to the brain.
The inner ear also houses the vestibular system, responsible for our sense of balance. The semicircular canals detect rotational movement, while the utricle and saccule sense linear acceleration.
The ear is a fragile sensory organ. Trauma, infection, or structural abnormalities can disrupt its intricate functions, leading to hearing loss, dizziness, or balance problems. Understanding its anatomy is therefore crucial for preserving optimal ear health and preventing potential impairments.
Common Ear Conditions: Unveiling Symptoms and Impacts
When it comes to our sensory organs, our ears play a crucial role in maintaining balance, hearing, and spatial awareness. However, these delicate structures are susceptible to various injuries and conditions, affecting our daily well-being. In this article, we delve into three common ear conditions – perichondritis, hematoma, and cauliflower ear – uncovering their symptoms, causes, and potential consequences.
1. Perichondritis: The Inflammation of the Ear’s Protective Layer
Perichondritis is a painful inflammation of the perichondrium, a thin layer of tissue covering the cartilage of the ear. This condition typically arises from bacterial infections, most often caused by a Pseudomonas bacteria. Common symptoms include:
- Intense pain and tenderness in the affected ear
- Redness, swelling, and warmth around the ear
- Fever and chills
- Pus drainage from the ear canal
- Hearing loss in severe cases
Left untreated, perichondritis can lead to permanent damage to the ear cartilage, potentially resulting in misshapen ears or hearing impairments.
2. Hematoma: A Painful Collection of Blood
A hematoma occurs when blood accumulates in a pocket between the cartilage and the perichondrium of the ear. This condition is commonly caused by blunt force trauma, such as a blow to the ear or excessive ear piercing. Symptoms include:
- Severe pain and swelling in the affected area
- Darkening or discoloration of the ear
- Decreased hearing
- A feeling of pressure or fullness in the ear
- Ringing or buzzing sounds
If not addressed promptly, a hematoma can lead to infection or scarring, potentially affecting the shape of the ear.
3. Cauliflower Ear: A Chronic Disfigurement of the Ear Cartilage
Cauliflower ear is a permanent deformity of the outer ear, characterized by a thick, bulbous appearance. It is predominantly caused by repeated trauma to the ear cartilage, often seen in contact sports like wrestling or boxing. Symptoms may include:
- Swelling, bruising, and tenderness in the ear
- The thickening and hardening of ear cartilage
- A cauliflower-like appearance of the ear
- Pain and discomfort
Cauliflower ear is a progressively disfiguring condition that cannot be fully reversed. Prevention is paramount, and athletes should wear protective headgear during contact sports to minimize the risk of ear injuries.
Treatment and Prevention: Restoring Ear Health
When the ear endures an injury, timely and effective treatment is crucial to restore its health. The arsenal of treatment options at our disposal includes aspiration, incision and drainage, antibiotics, and in severe cases, surgical repair.
Aspiration is a minimally invasive procedure that involves extracting fluid buildup from the ear using a needle. This technique is often employed to treat perichondritis, an infection characterized by fluid accumulation between the cartilage and skin of the ear.
Incision and Drainage is a more involved procedure that requires making an incision to drain the infected material. This method is typically used for hematomas, which are collections of blood in the ear that can obstruct hearing and cause pain.
Antibiotics play a vital role in combating bacterial infections that may arise from ear injuries. Oral or topical antibiotics are prescribed to target and eliminate the infectious agents, preventing further complications.
In some severe cases, Surgical Repair may be necessary to address extensive tissue damage or correct anatomical abnormalities caused by the injury. This type of intervention aims to restore the ear’s structure and functionality.
Beyond medical intervention, prevention plays a pivotal role in safeguarding ear health. Wearing protective headgear during contact sports, such as wrestling and football, is paramount to minimize the risk of head and ear injuries. Furthermore, unnecessary ear piercings should be avoided, especially in unsterile environments, as they can introduce infection to the delicate ear tissue.
Promptly addressing ear injuries or infections is crucial to prevent long-term complications. If you experience any ear pain, swelling, or hearing loss, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment will enhance the chances of a full and speedy recovery, ensuring the preservation of your ear’s health.
Professional Involvement: Ensuring Ear Health
- Highlight the role of sports coaches, athletic trainers, sports medicine providers, ear piercing professionals, and insurance companies in preventing, diagnosing, and treating ear injuries.
Professional Involvement: Ensuring Ear Health
Sports Coaches and Athletic Trainers
Sports coaches and athletic trainers play a crucial role in preventing ear injuries in athletes. They enforce proper technique during tackling and other high-impact maneuvers, minimize player-to-player contact, and encourage the use of appropriate headgear. Athletic trainers are trained to assess and care for ear injuries on the field, reducing the severity and likelihood of long-term complications.
Sports Medicine Providers
Sports medicine providers, including physicians and physical therapists, diagnose and treat ear injuries. They determine the appropriate course of treatment, whether it be conservative (e.g., rest, ice, compression) or surgical. They also provide guidance on rehabilitation and injury prevention strategies to help athletes return to play safely.
Ear Piercing Professionals
Ear piercing professionals are responsible for ensuring that earlobe piercings are performed in a sterile environment using clean equipment. They provide detailed instructions on aftercare and advise clients on what to look for regarding signs of infection. By adhering to best practices, ear piercing professionals help prevent ear injuries such as infections and trauma.
Insurance Companies
Insurance companies play a vital role in covering the costs associated with ear injuries. They provide financial support for medical treatment, rehabilitation therapies, and surgical procedures. This coverage ensures that athletes have access to the necessary care to heal their injuries and prevent long-term complications.